We had published the Glossary of Motorcycle Terms (A-B) previously, so let us continue with the series, this time for terms beginning with the letter “C.”
Café Racer:
The café racer style of motorcycle originated in the 1960s and is known for its stripped-down appearance, low-slung handlebars, and rear-set footpegs. It is said that they were modified from standard bikes for racing between cafés.

Cage:
Bikers refer to a car as a “cage” since it traps the occupants inside rather being exposed to the environment.

Caliper:
Refer to “Brake Caliper” in the previous article. Anyway, the caliper consists of several other parts including the piston(s) that push the brake pads against the brake disc (a.k.a. rotor).

Camshaft (cam), cam lobes:
A spinning metal shaft with oval cam lobes to open the valves in a four-stroke engine.

cc:
“CC,” written in small letters as “cc” refers to the engine’s displacement in cubic centimetres. It is also the measurement for the amount of fluids.

ci:
CC is a metric measurement, so the imperial measurement is “ci” (cubic inch). It was formerly used by many motorcycle makers, but it is now only limited to Harley-Davidson and Indian Motorcycles. 1 ci = 16.39 cc.

Carburetor/Carb:
A carburetor is a mechanical device for mixing air and fuel in the correct ratio for combustion in an internal combustion engine. Virtually all motorcycles are fuel injected these days, apart from a few budget ones that still use the carb.
CE protector:
Also known as CE-certified motorcycle armour, it refers to protective paddings in motorcycle gear. CE stands for Conformité Européene in French, which translates to European Conformity. CE certification ensures the armour meets specific safety requirements and has undergone testing to validate its protective qualities.

Center stand:
Colloquially called the “full stand” here, a center stand is the large, double-legged, fold-out motorcycle stand, mostly found on small cc, adventure, sport-touring, and touring bikes.

Chain drive:
The chain connecting the front small sprocket on the bike’s transmission output shaft to a larger sprocket mounted to the rear wheel hub, to transfer the engine’s torque and power to the rear wheel.

Chassis:
The frame or structure of a motorcycle that act as the central component to where various components such as the engine, suspension, wheels, and bodywork are connected.

Chatter:
Mechanical oscillation or vibration with a bike. Also a term that describes oscillation or vibrations from the tyres.

Chicken strips:
The untouched outer sections of the motorcycle’s tyres, due to lack of cornering angle. “Chicken” here alludes to being less than brave.

Choke:
A mechanism or plate in a carburetor that restricts the airflow during cold engine starting and warm-up. Limiting the air amount of air “enriches” the air-fuel mixture (more fuel). The choke must be deactivated when the engine is sufficiently warm to run smoothly.

Chopper:
A motorcycle with its non-essential parts “chopped” (stripped) to lighten it, making it faster. However, the chopper styling now includes lengthened and raked forks.

Clip-ons:
Motorcycle handlebars clamped around the top of the bike’s fork tubes instead of being bolted to the top triple-clamp. Usually for sportbikes and café racers.

Clutch:
The device that engages and disengages the power transfer from the engine to the transmission. It allows for smooth gears changes plus control of power delivery to the driving wheel.

Compression damping:
Rate the suspension (forks and rear shock) compresses when contacting a bump.

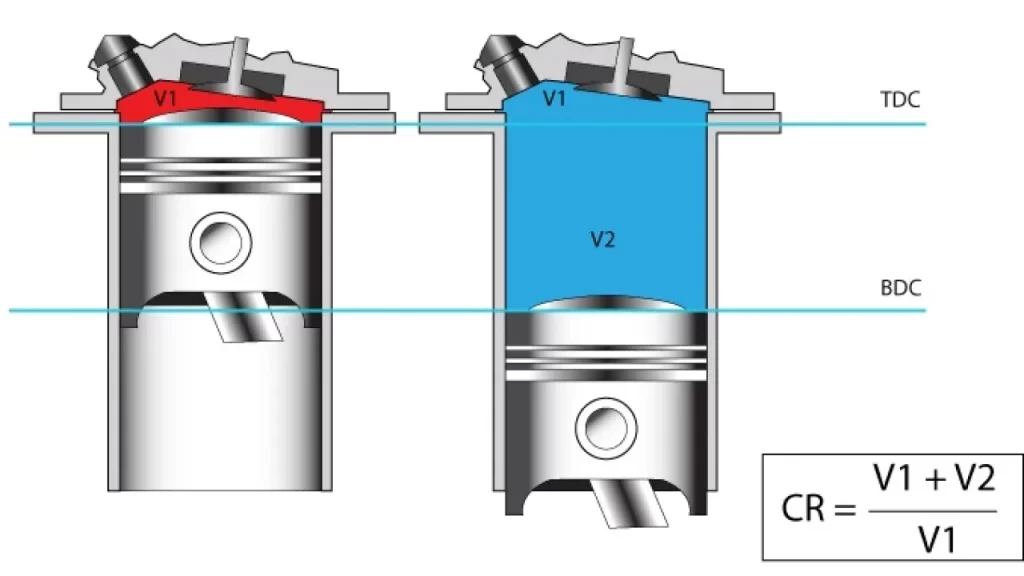
Compression ratio:
In simple terms, it describes how much the fuel-air mixture gets compressed when the engine’s piston rises to its highest point (TDC/top dead centre). The ratio is derived by dividing the cylinder’s volume at the piston’s lowest point in the stroke (BDC/bottom dead centre) to the volume when the piston is at TDC.
Compression release:
Also known as a decompression valve or a decompressor, this mechanism is used to reduce compression pressure for easier starting. It is commonly found in large single-cylinder engines (a.k.a. thumpers).
Counterbalancer:
Also known as a balance shaft, it is mounted in then engine to reduce vibrations and improve engine smoothness, by counteracting vibrations in engines with unevenly spaced cylinders, such as (narrow spaced) V-twins, triples, and parallel-twins.

Countersteer:
Counter-steering is the technique to initiate a turn. It involves briefly steering the handlebars in the opposite direction of the intended turn, causing the motorcycle to lean in the desired direction and initiate the turn. In other words, push left to go left, push right to go right.

Cowl/Cowling:
Also known as the fairing, it is a piece of bodywork to cover certain parts of a motorcycle. It serves multiple purposes, including enhancing the aesthetics of the bike, improving aerodynamics, insulate the rider from wind blast, and protect internal components.

Crash bars:
Engine guards, or frame sliders, are protective bars mounted to a motorcycle’s frame to minimise damage to the motorcycle in the event of a tip-over, low-side, or other types of accidents.

Cruiser:
A style of motorcycle known for its laid-back and relaxed riding posture. It is designed with a comfortable riding position, low seat height, and emphasis on style and aesthetics. Cruisers are often associated with a classic and timeless look.