While we revel at the current Ducati’s V4 lineup consisting of the Panigale V4, Streetfighter V4, Multistrada V4, and most recently the Diavel V4, Ducati had actually made a V4 engine even prior to producing their first V-Twin engine. Instead, perhaps ironically, it was the V-Twin that went on to bring the Ducati name to the masses, before they went back to the V4 to dominate the world’s racing circuits. The answer has to do with the machine the engine was fitted to: The Ducati Berliner 1260 Apollo which debuted in 1964.
How it began
Ducati’s United States distributor, the brothers Joe and Mike Berliner of Berliner Motor Corporation were convinced they could sell motorcycles to the American police departments. But they had to compete with Harley-Davidson who had a free run in that segment.
So, Joe Berliner approached Ducati in 1959 with a proposal to build that bike. Ducati was owned by the Italian government at the time and produced only the 20occ Elite. And, they were also in a bad state as with all other Italian motorcycle manufacturers who had to contend with the Fiat 500’s popularity.

However, official US police department specifications were increasingly standardised across the country, and naturally favoured their national product i.e. Harley. They required an engine capacity of at least 1200cc, a minimum 60-inch/1525mm wheelbase, and 5.00-inch x 16-inch tyres.
Mike Berliner shipped two Harley FL Duo Glides to Ducati for evaluation. After considering the design of the archaic 74 cubic inch (1212cc) Harley FL’s engine, Ducati’s chief Dr. Giuseppe Montano and chief engineer Dr. Fabio Taglioni agreed they could produce a more efficient and modern design. Taglioni eagerly accepted the commission as a technical challenge.

Unfortunately the bureaucrats in Rome showed much scepticism which resulted in dragged out negotiations until 1961 before Montana got the green light, and after Berliner promised to underwrite the project including development and production costs.
The name Apollo was chosen by the Berliner brothers in honour of the Apollo moon program which had just begun.
The engine and its performance
Taglioni was told to make the big bigger and faster and so, he designed a 1257cc, air-cooled, two-valved, 90° V4, with a 180 crankshaft. The bores and strokes were 84.5 mm and 56 mm, respectively, making it the most oversquare Ducati engine at the time. Valve actuation was handled by pushrods and rocker arms, rather than tower shafts and bevel gears. It made 100 hp at just 7,000 RPM.
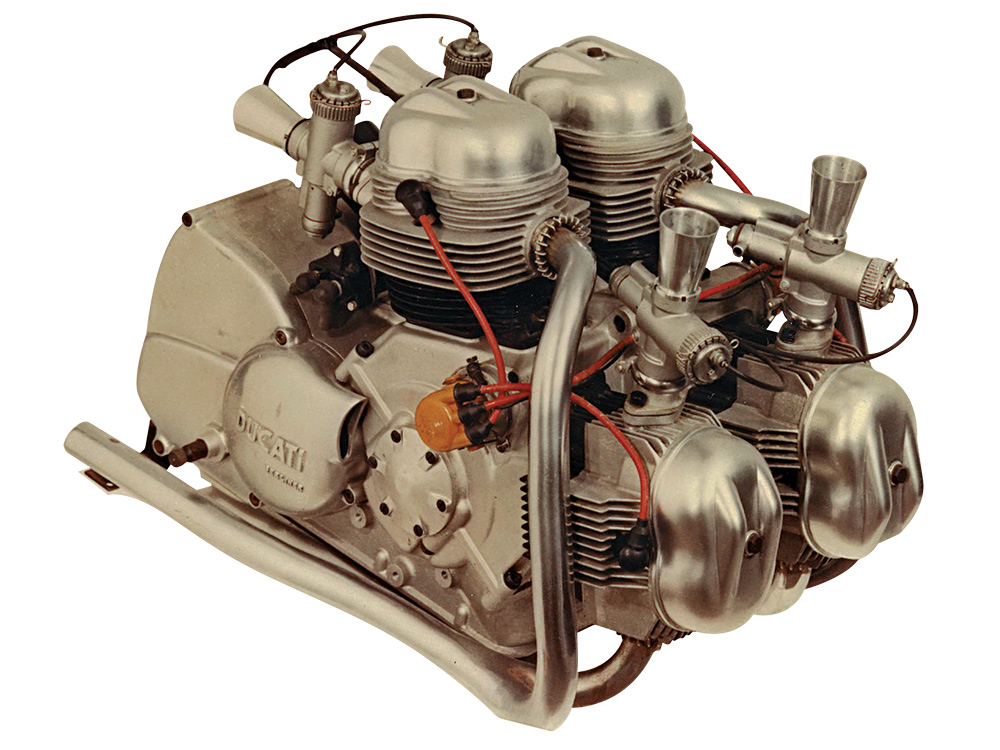
Ducati gave it a 5-speed transmission to up the ante against their rivals who had 4-speed gearboxes. Taglioni even designed a provision to fit an automatic (CVT) in the future.
The engine was mounted in a heavy duty open cradle frame. There was a kick starter for the brave or with steel shins, but there was also an electric starter which looks similar to the Fiat TV1100’s. There was a massive 200w generator on the right side to cater for all the police electrical equipment. Ceriani developed the suspension, and front and rear single leading show drum brakes.
Weigh was finally tallied at 270 kg, dry. Although that is a lot even by today’s standards, it was actually lighter than the Harley’s 291 kg.
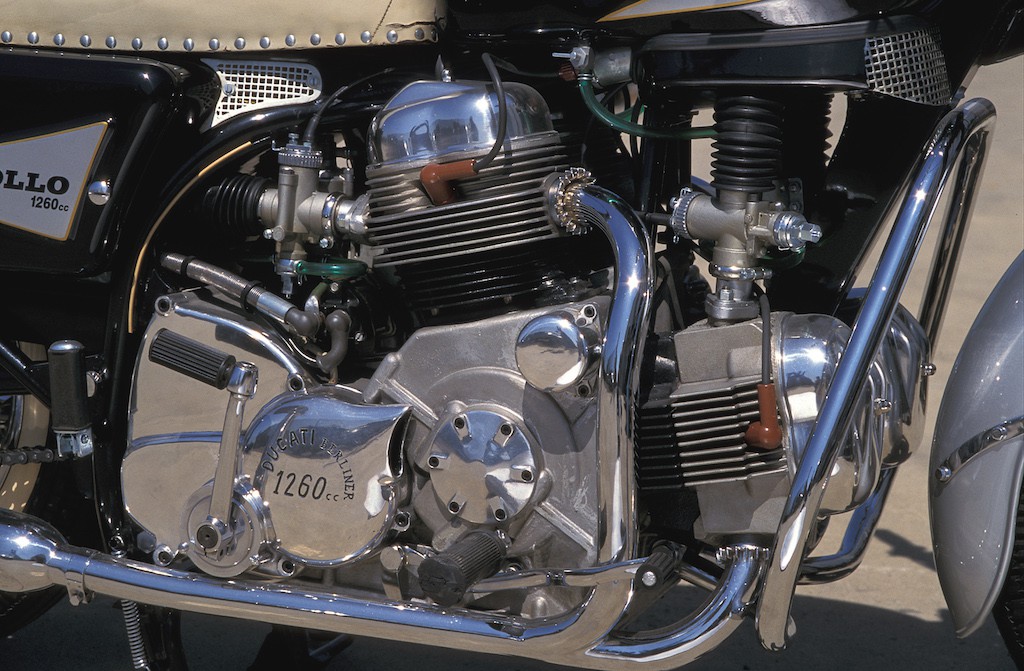

Ducati completed the bike’s styling with a peanut-style fuel tank, cowboy seat with a chrome cage grab rail, and forks and shocks that look similar to the FL’s.
Two fully working prototypes were built, one was painted gold for Berliner to demonstrate at shows, while another in black and silver. There were also two extra spare engines.
The test
So, off went Ducati’s test rider Franco Farne on the bike’s maiden test, only for him to return with the verdict: “It handles like a truck.” But the Ducati Berliner 1260 Apollo made up for it in straight-line performance, where it hit more than 200 km/h. It confirmed that it was most powerful the fastest European bike.
Unfortunately, that amazing performance was also its downfall, especially because it was fitted with those 16-inch automobile tyres. Another Ducati tester, and former GP mechanic Giancarlo Fuzzi‚ went out for a high speed test on the Milan-Bologna autostrada when the whitewall rear Pirelli ballooned, detached its tread, and came off the rim at around 160 km/h. Fuzzi called his survival “a miracle.”
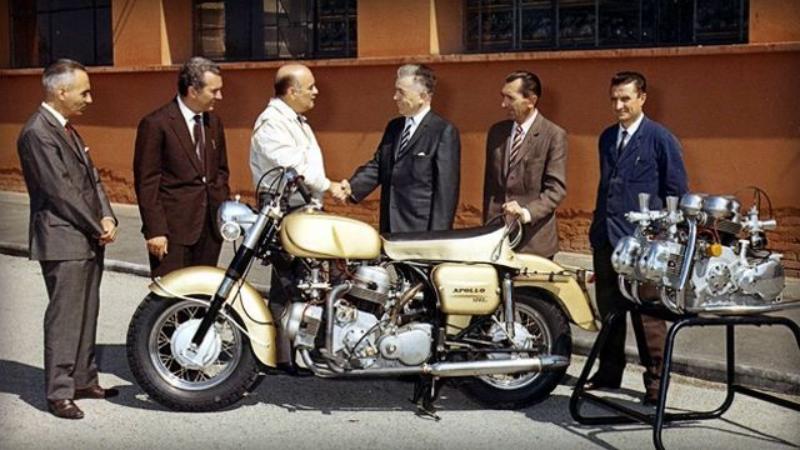

The engine was subsequently detuned to 80 hp by lowering the compression ratio and fitting less aggressive cams, but it was still too much for any tyre at the time. Again it was detuned by lowering the compression even more to 65 hp and tyre wear became “acceptable.”
By comparison, the Moto Guzzi Grand Prix 500cc V8 had 20-inch wheels, but its 78 hp also shredded the bike’s tyres.
The end of the project
Berliner was of course happy with the performance and went ahead to print flyers to sell the bike. They planned to sell the detuned ‘normale‘ version to civilians as a touring model, while reserving the fully powered ‘Sport‘ version for law enforcement. In fact, 65 hp from the V4 was still more powerful than Harley’s 55 hp.
However, the detuned version had to contend with other European bikes such as BMW and British Twins.

Harley could also undercut the Apollo’s price of USD 1,500 by saying that they offer something close to that performance and a much cheaper price.
Then the Italian government decided that the limited market did not justify the tooling costs of production, and withdrew project funding. This was a severe blow to Berliner’s business plans.
What it could have been
The Ducati Berliner 1260 Apollo could have been the very first ‘superbike’ had tyre technology been up to the task; that and if it had used 18-inch tyres instead. Instead, the Honda CB750 appeared in 1969 to claim the honour. Even then, it had only 68 hp and a top speed of 201 km/h. Heck, even the “groundbreaking” Kawasaki Z1’s 903cc inline-four in 1972 produced only 81 hp and a top speed of 209 km/h.

Years later, Honda and Suzuki would copy the V4’s design for them to dominate GP racing.
It was indeed as missed opportunity.
However, the V4 engine’s design led Taglioni to design the engine that would bring about Ducati’s dominance in the superbike racing: The 90º V-Twin. But it could be seen that the 1257cc V4 had a place in his heart, which one of the spare engines sat in his office until his retirement in 1984.

Today, the black and silver prototype is owned by Hiroaki Iwashita, and resides in his museum at Yufuin on the island of Kyushu, Japan.
The fate of the gold coloured prototype is unkown.