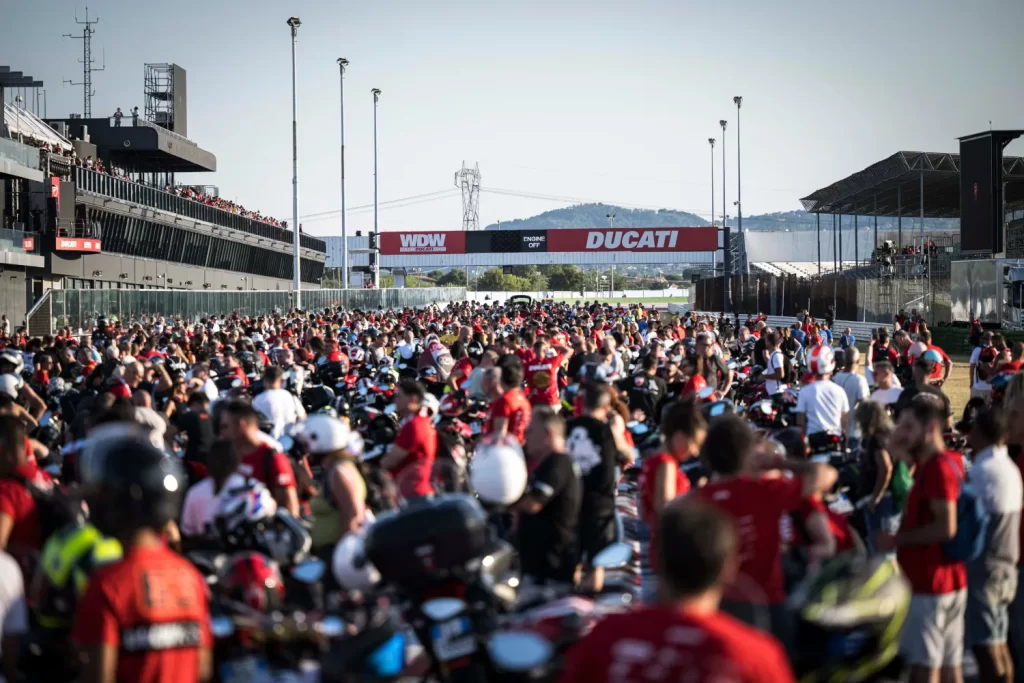
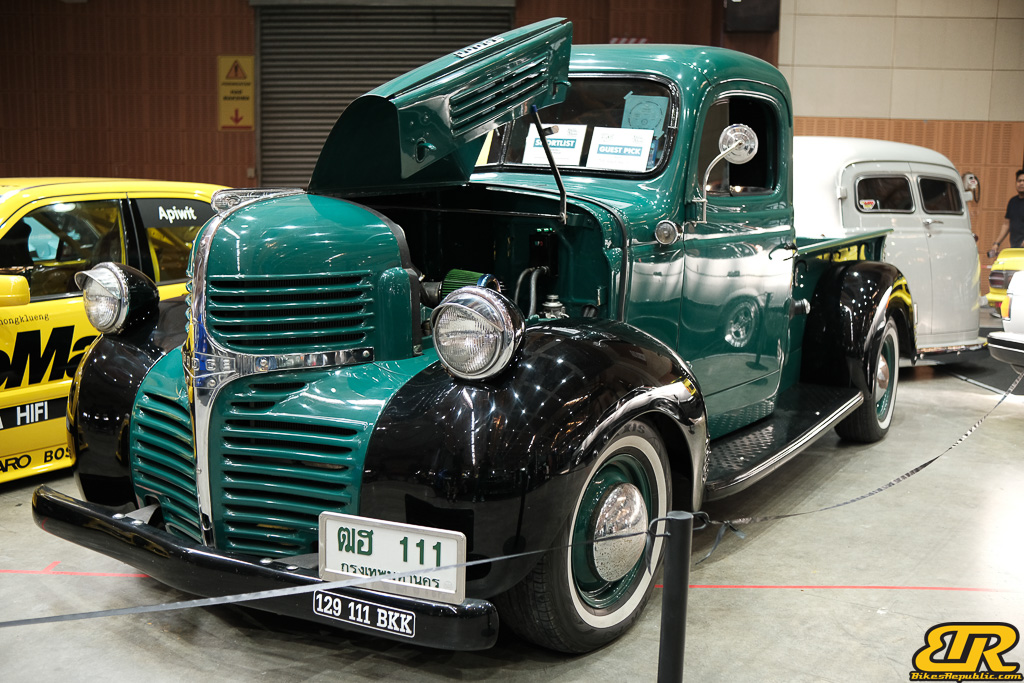
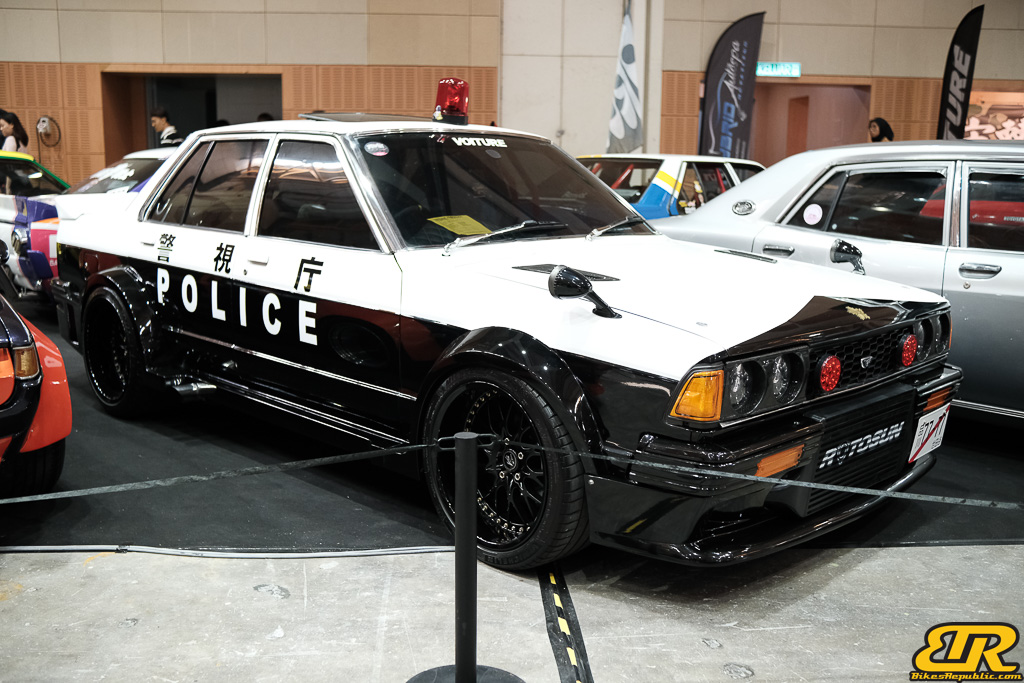
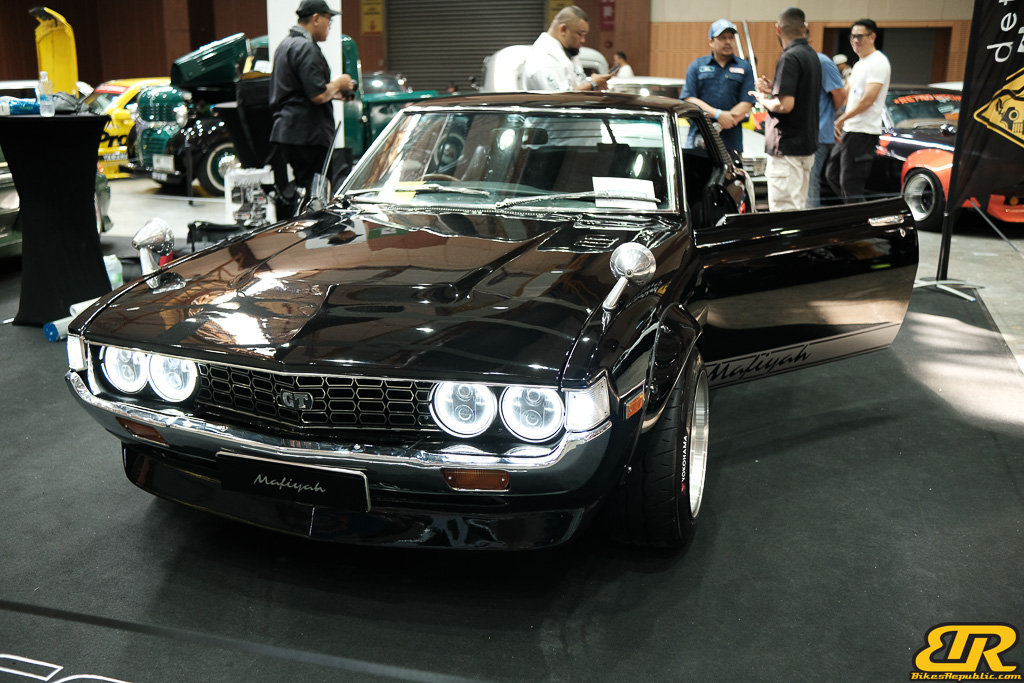
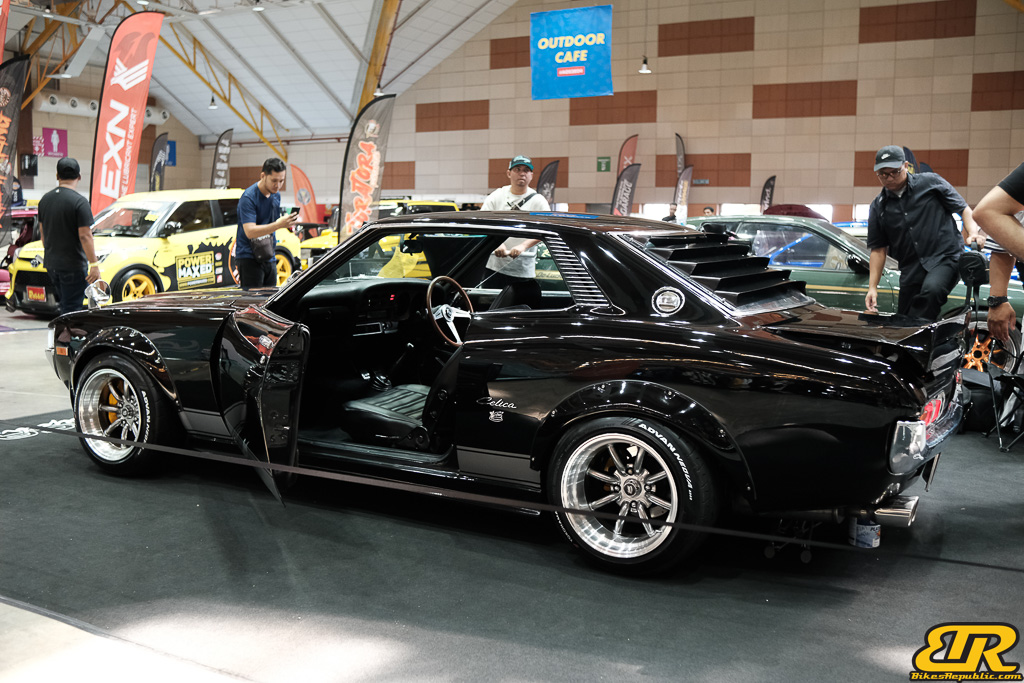
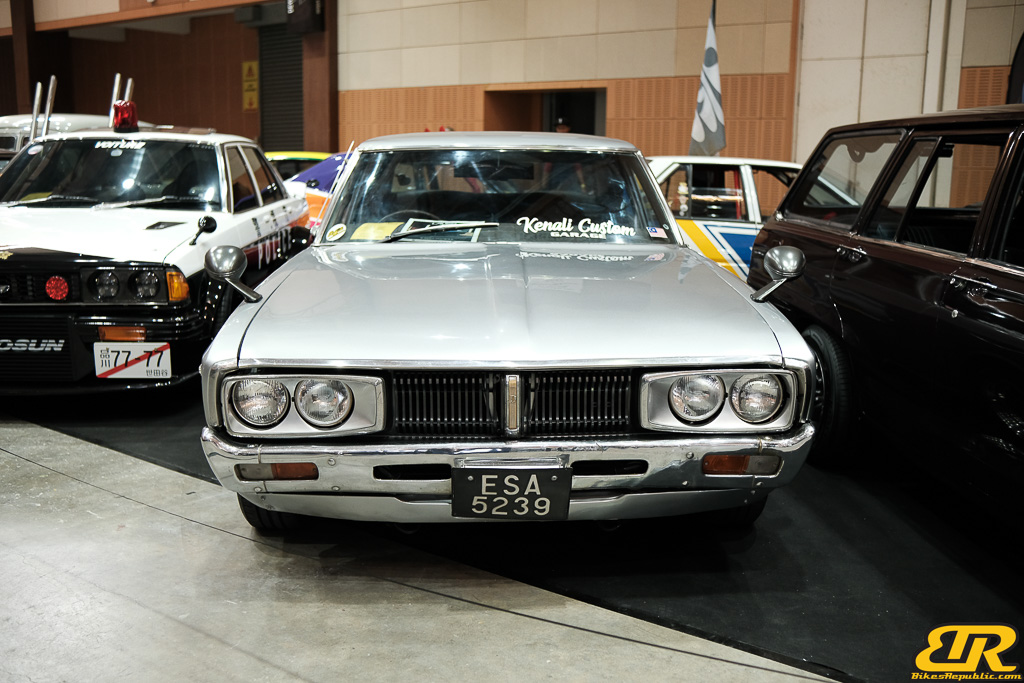
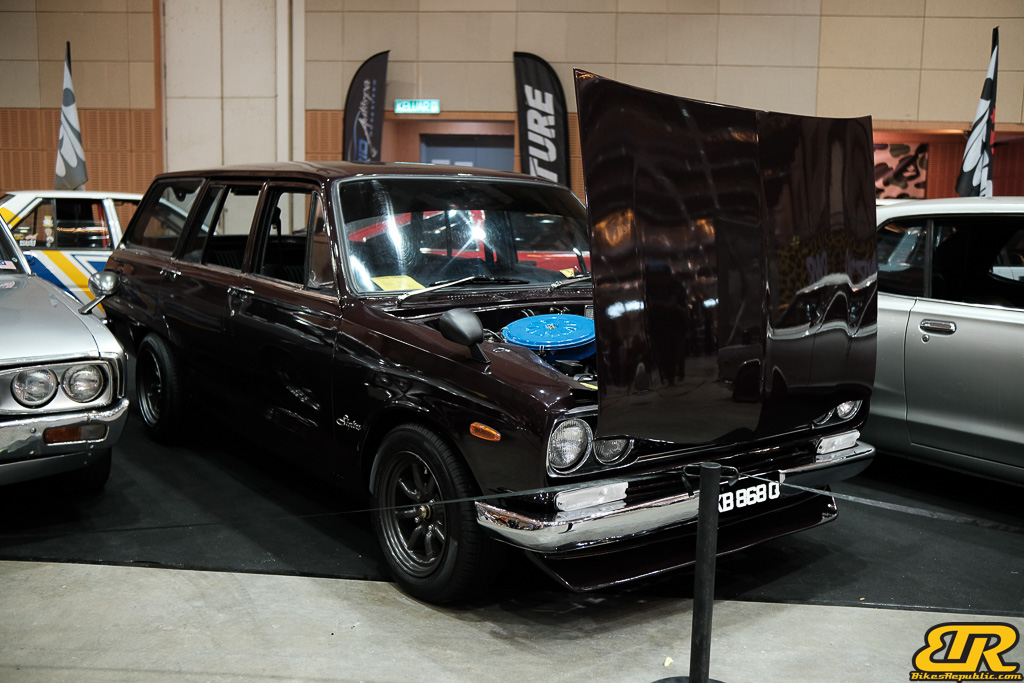
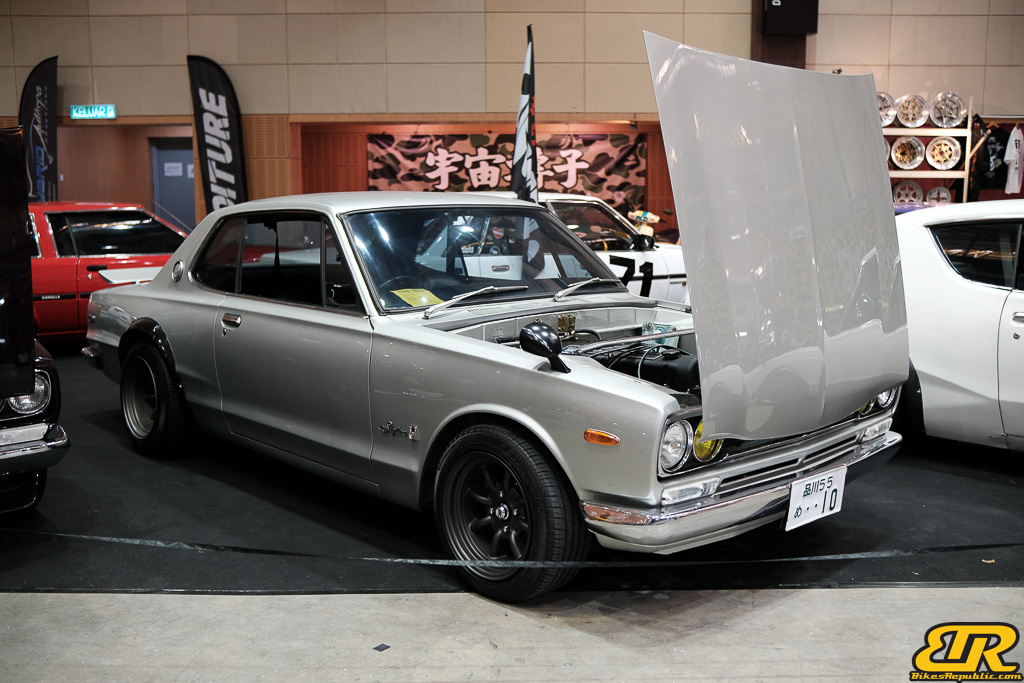
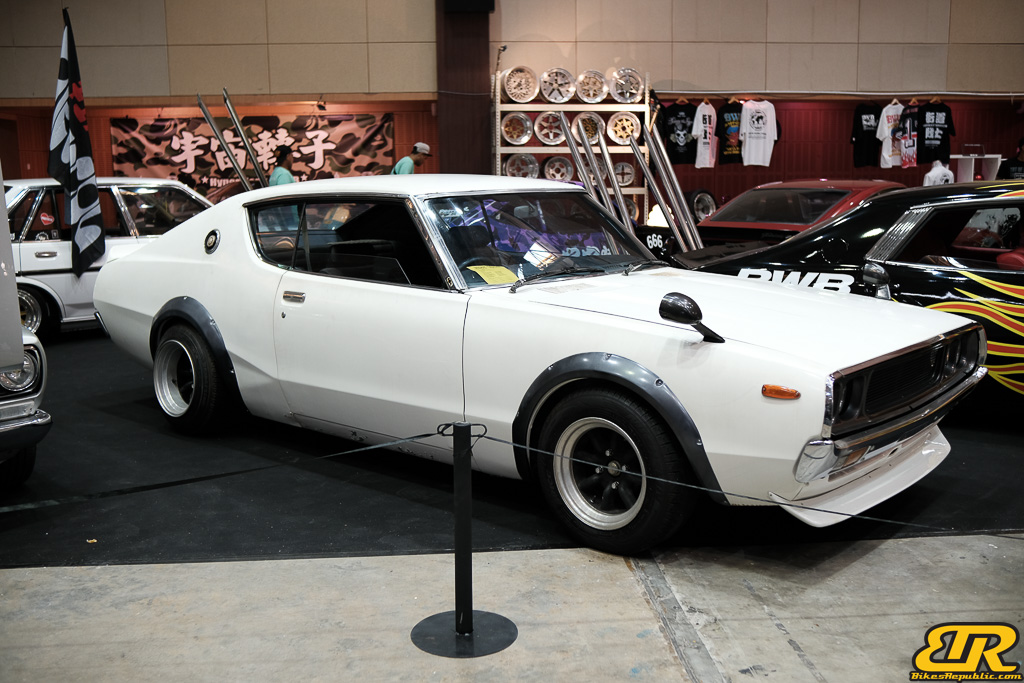
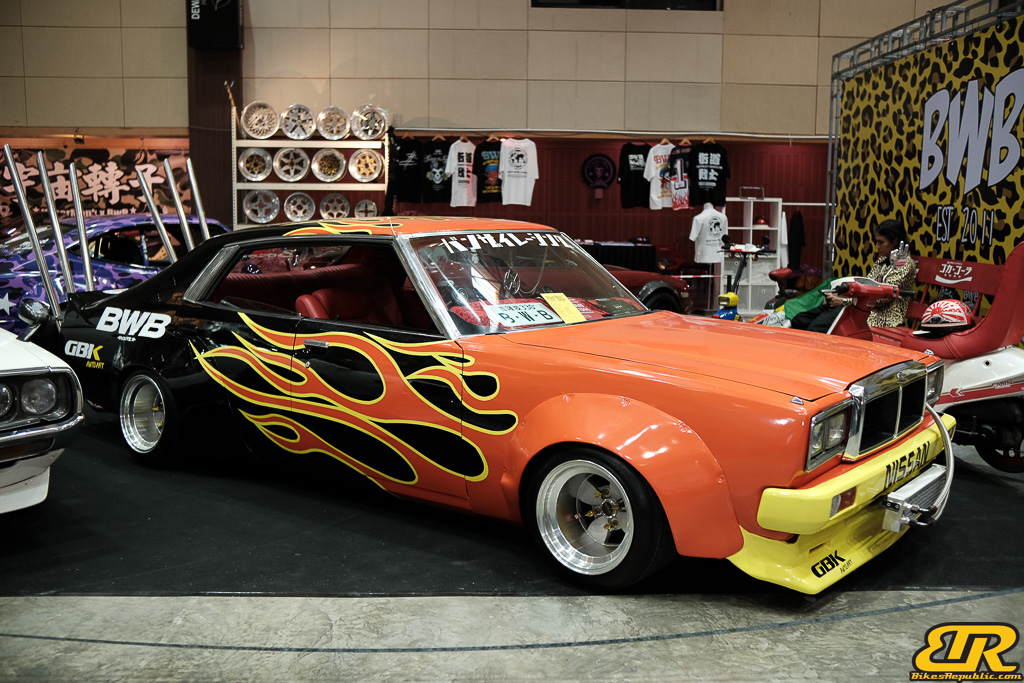
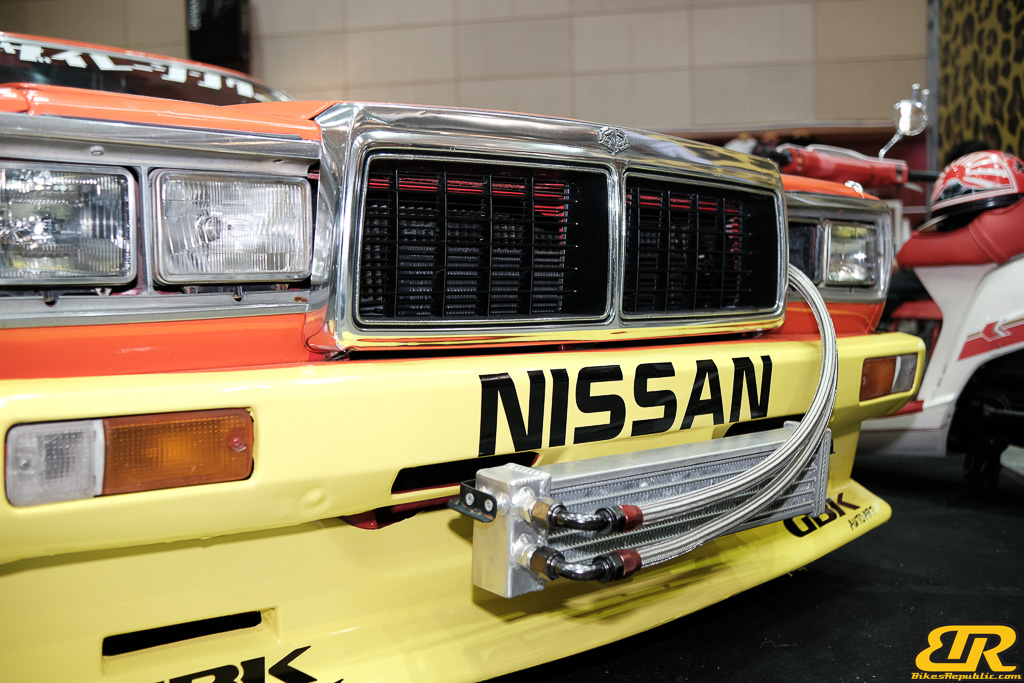
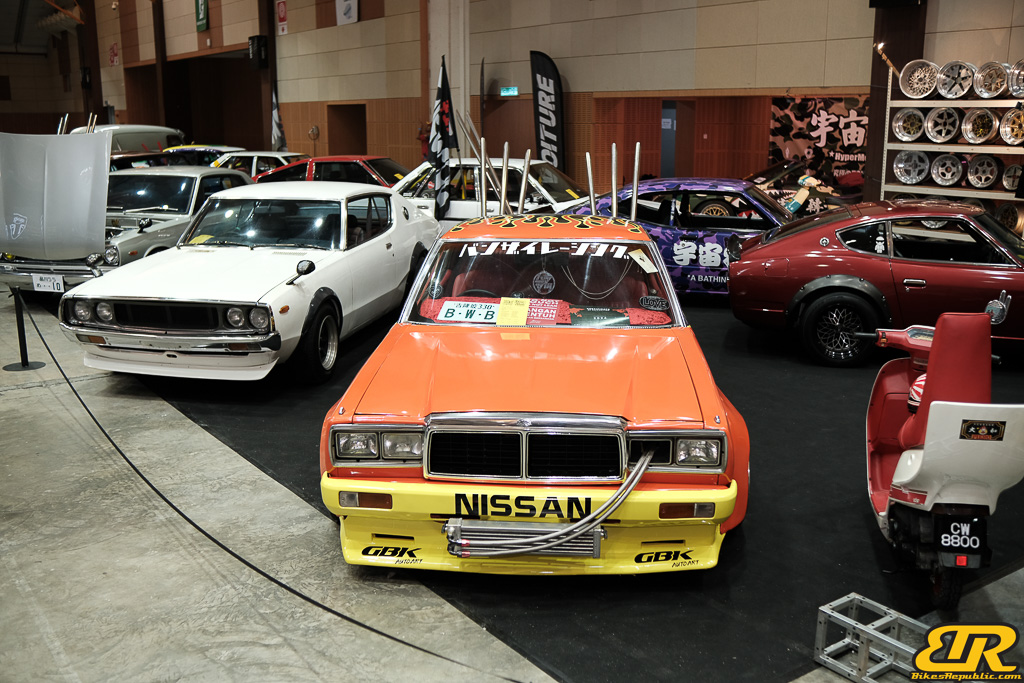
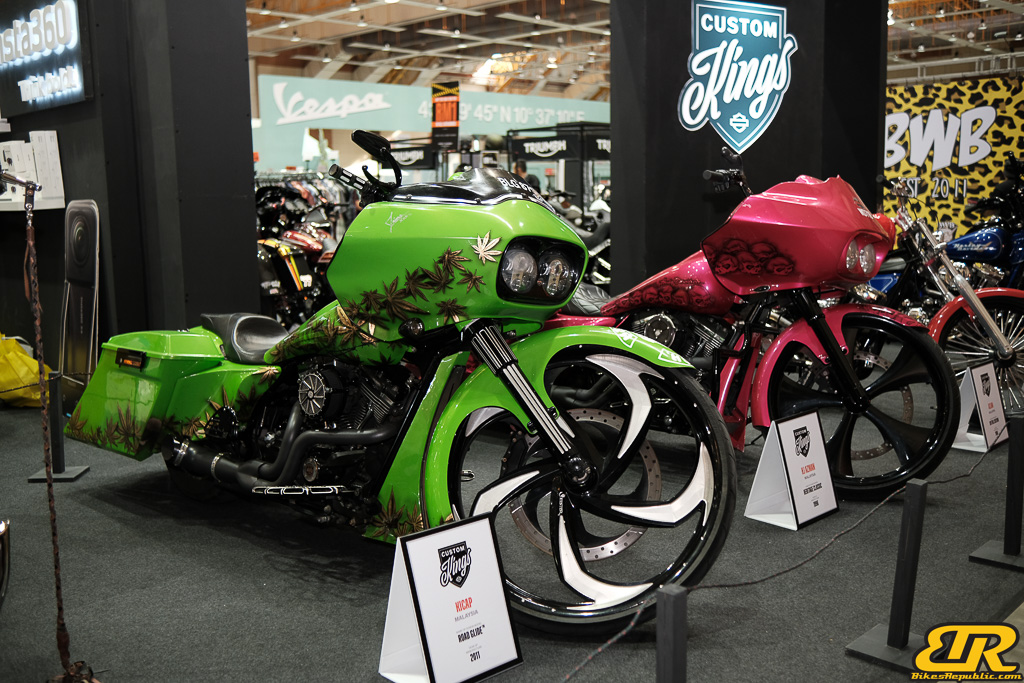
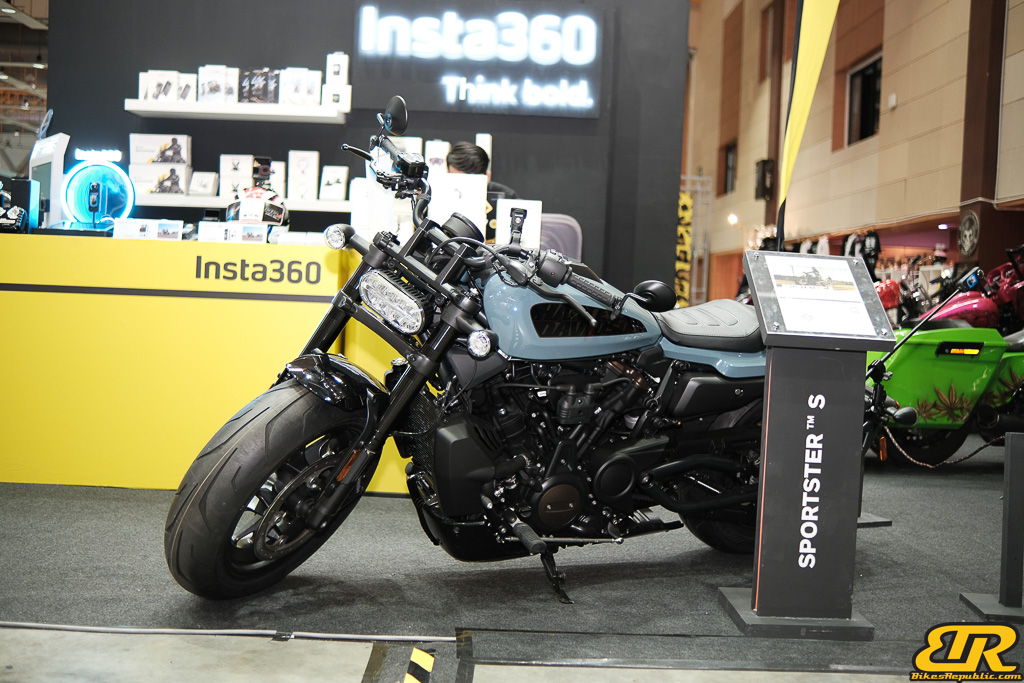
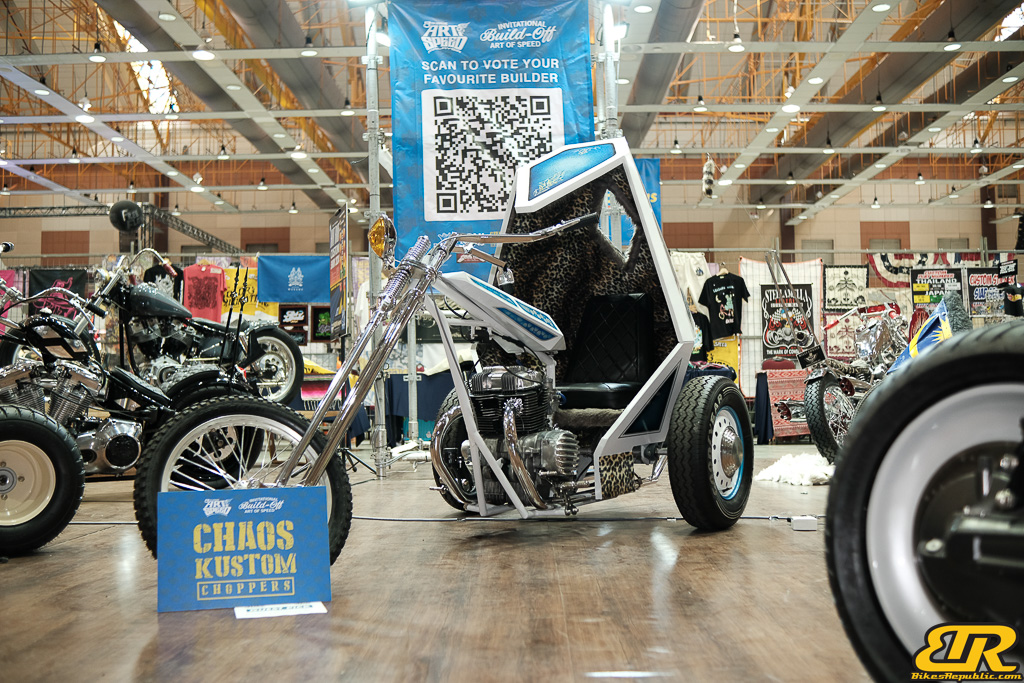
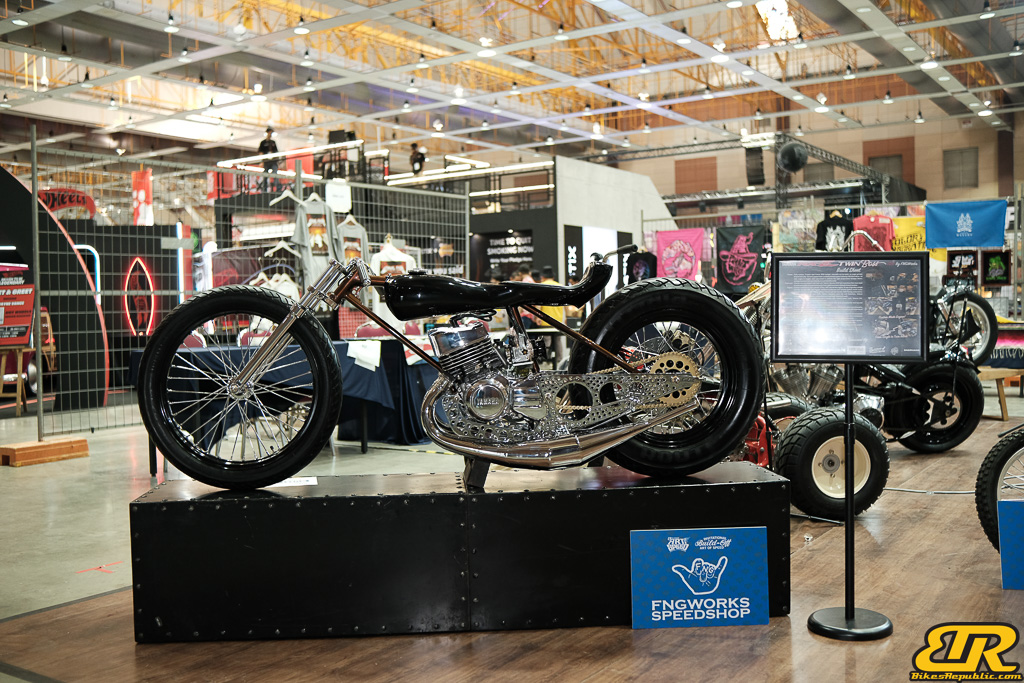
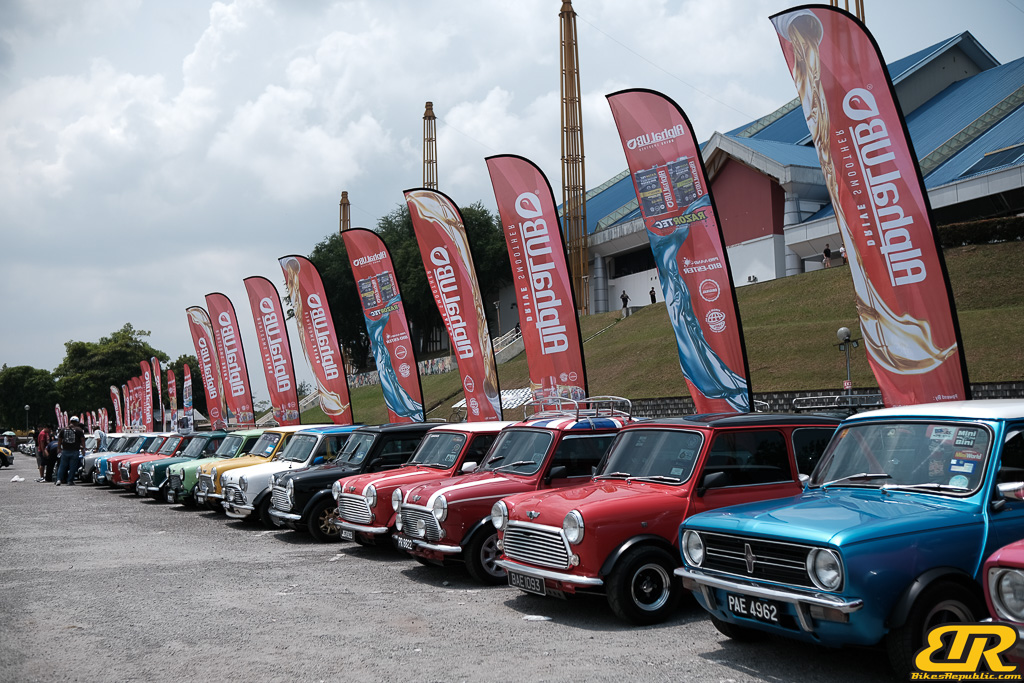
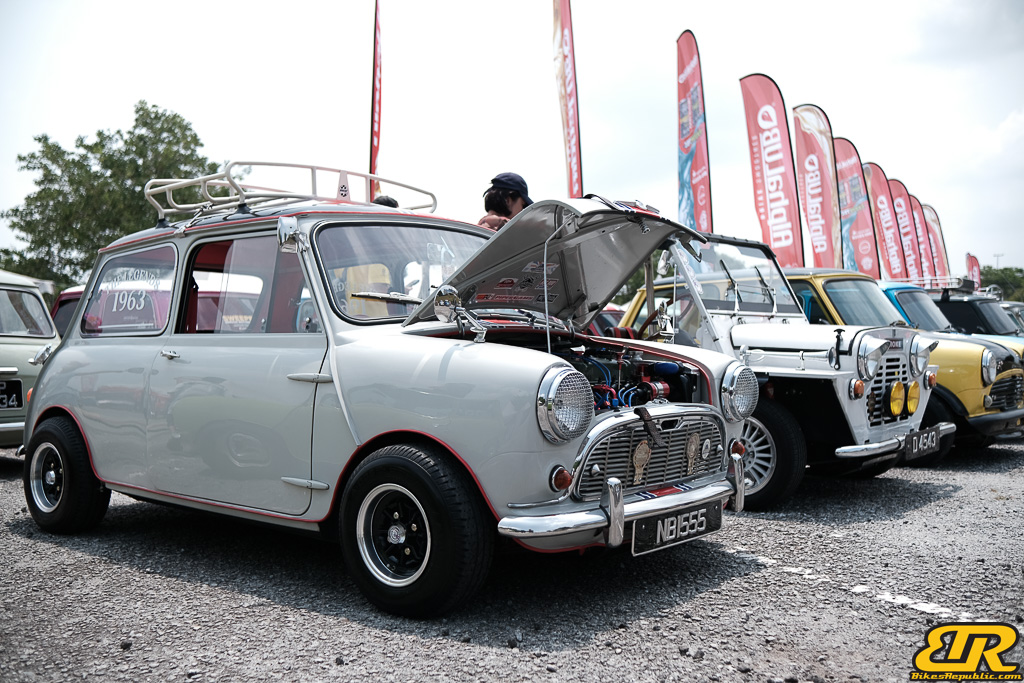
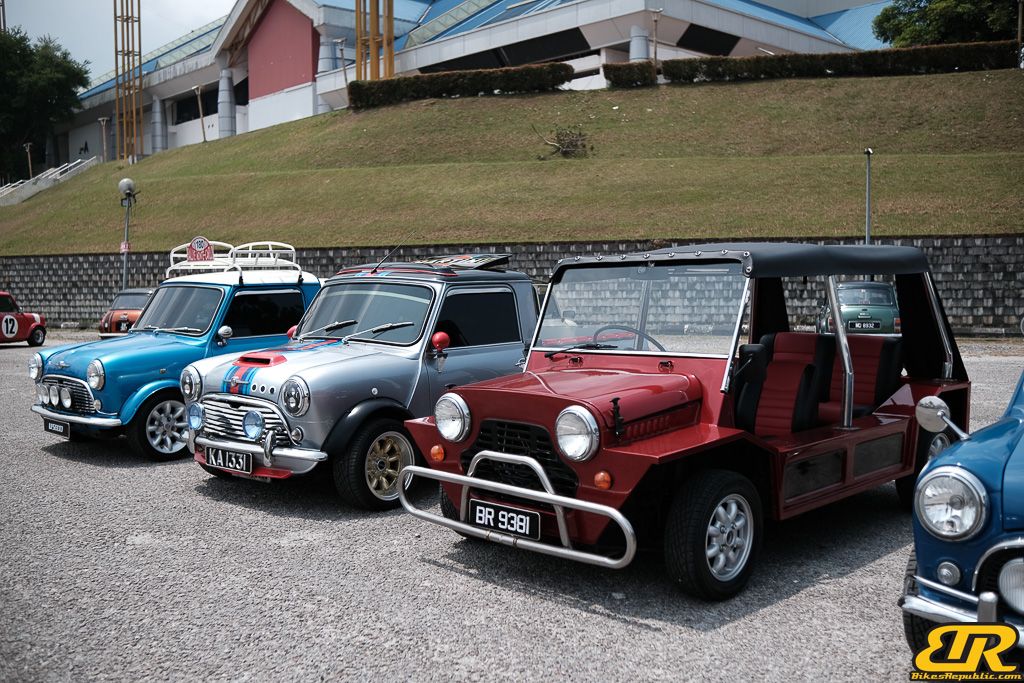
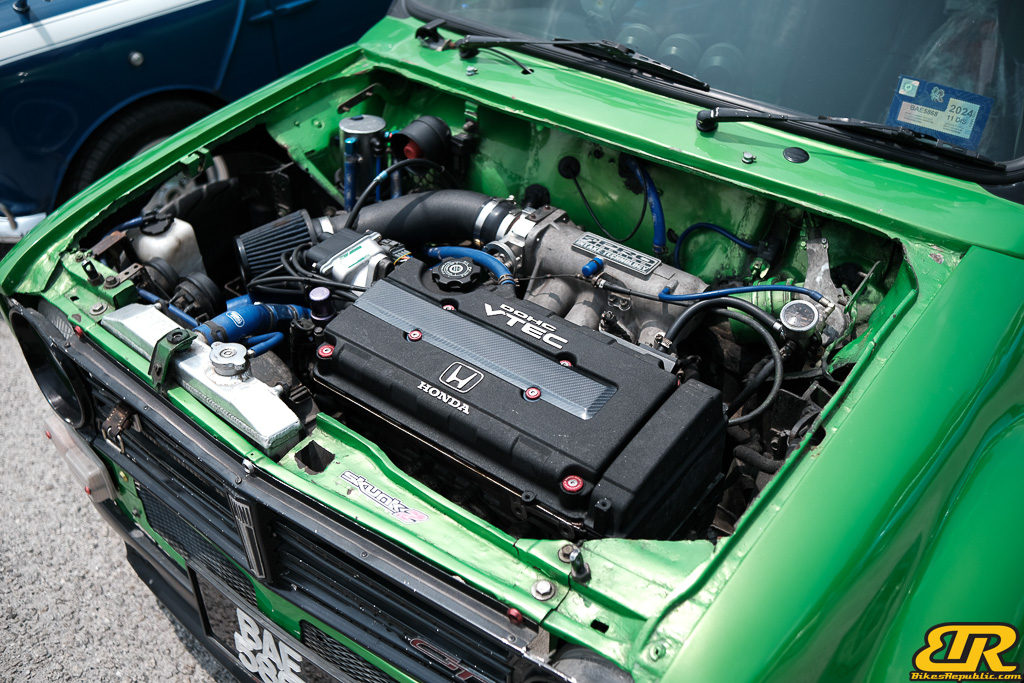
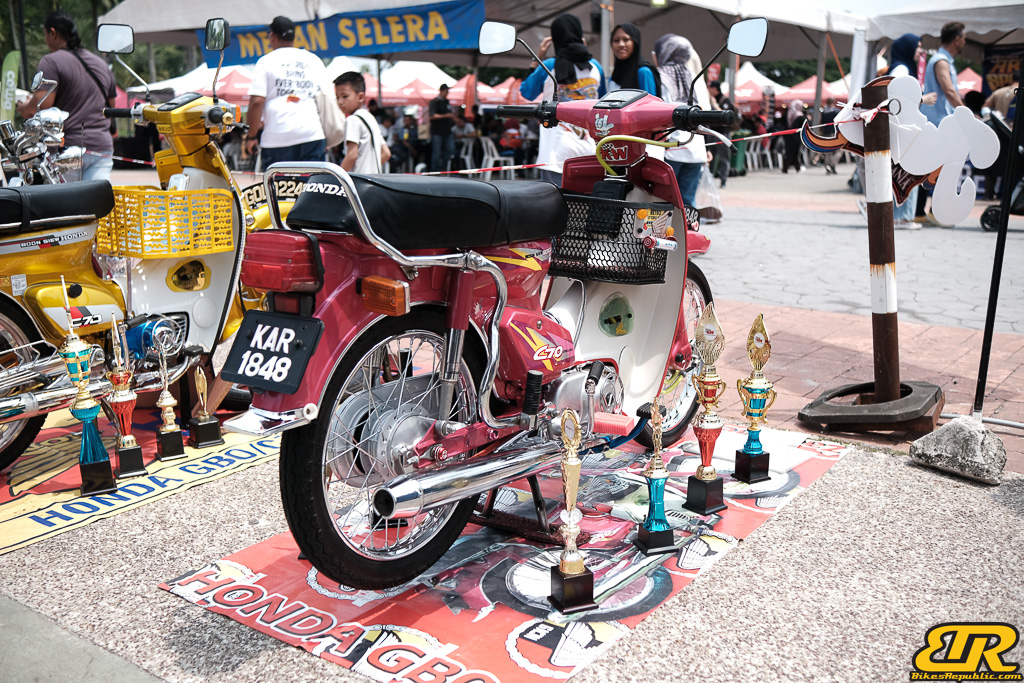
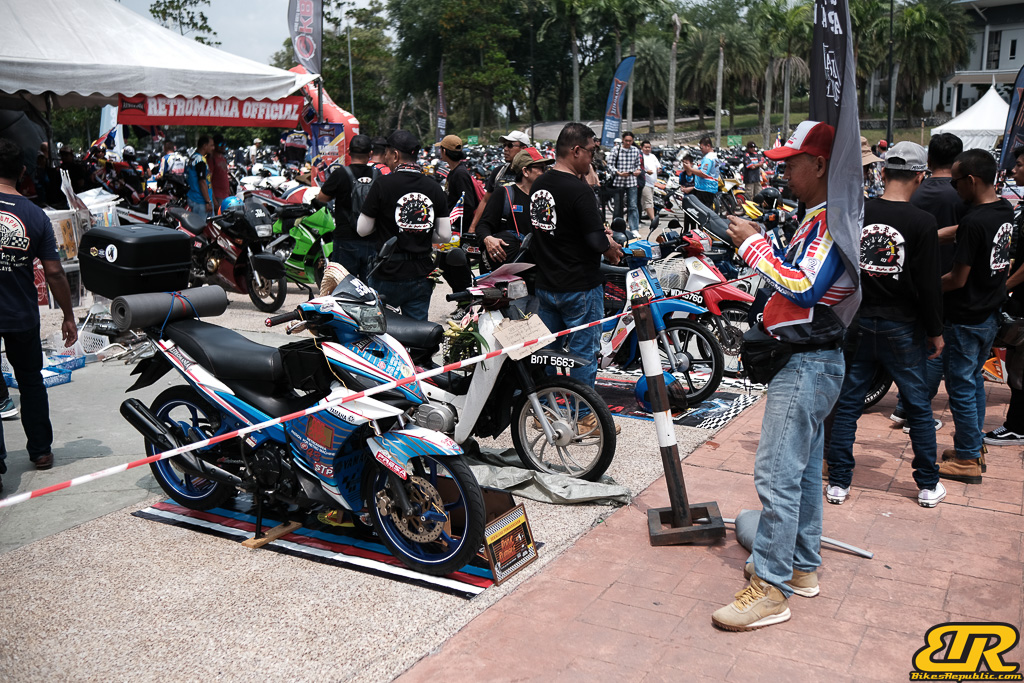
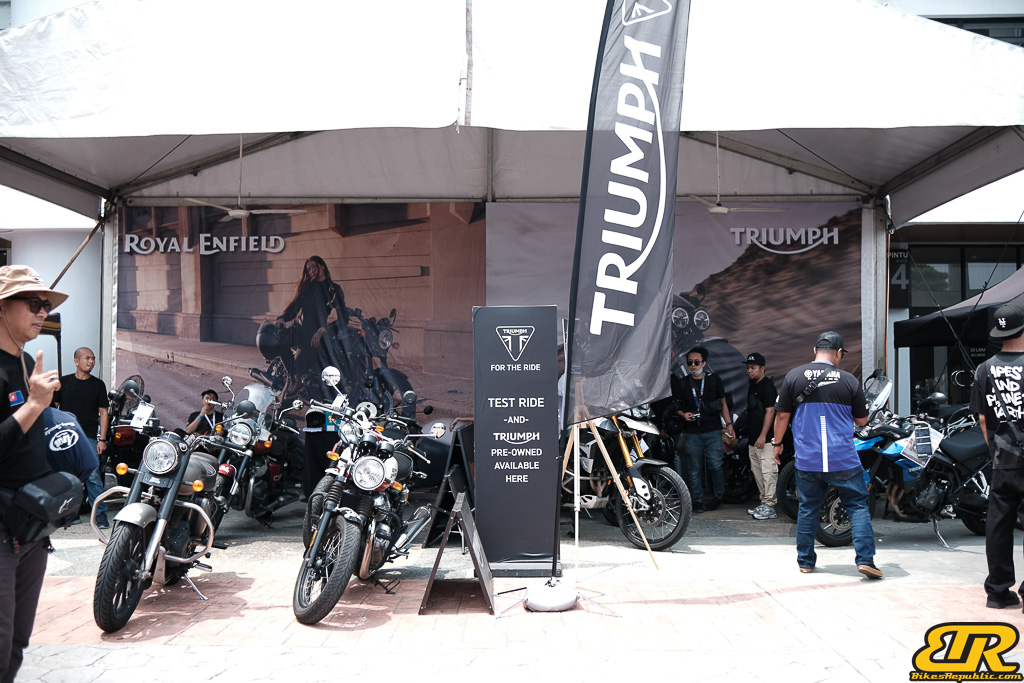
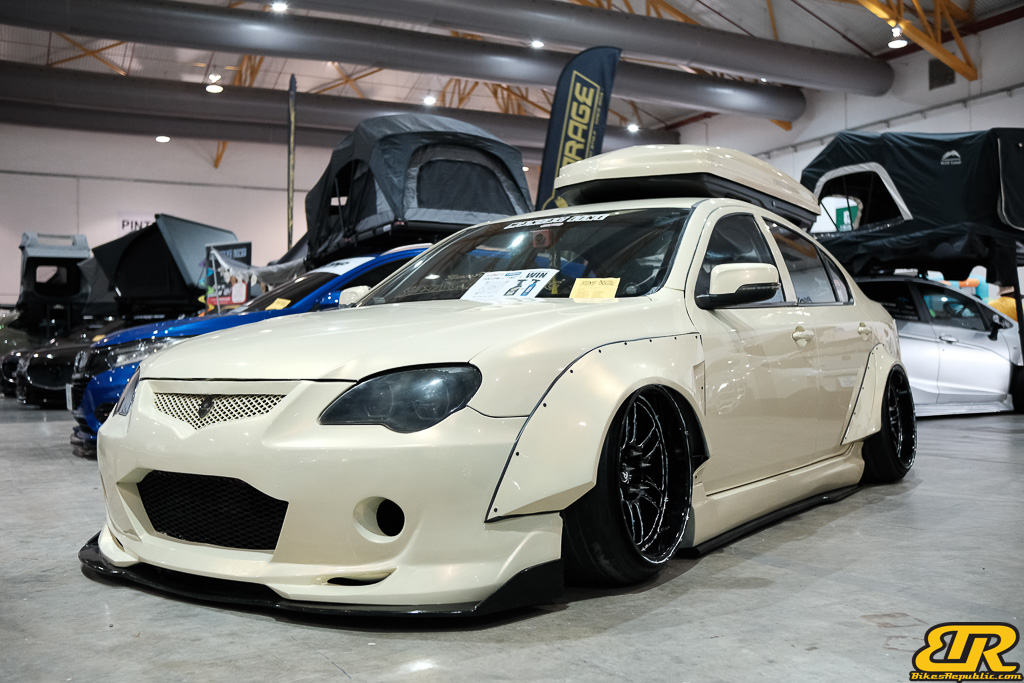
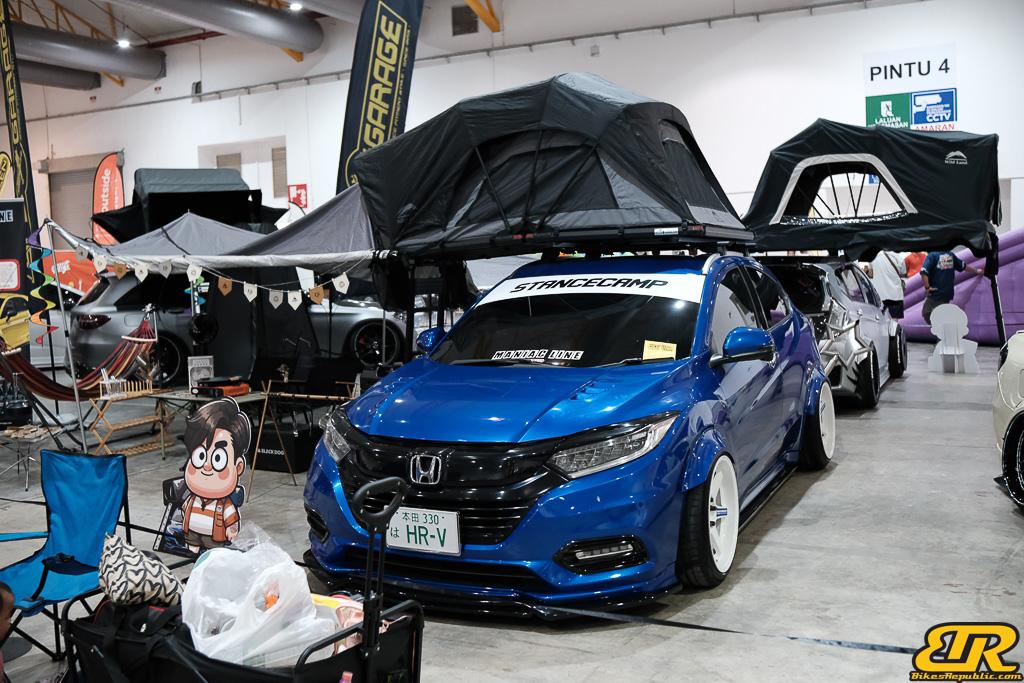
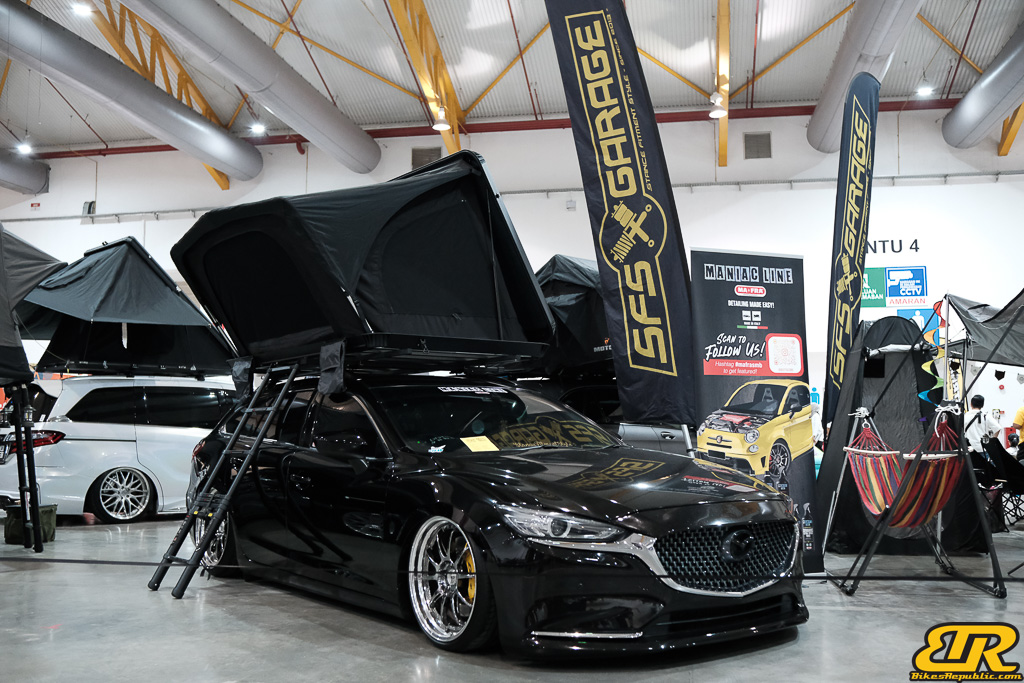
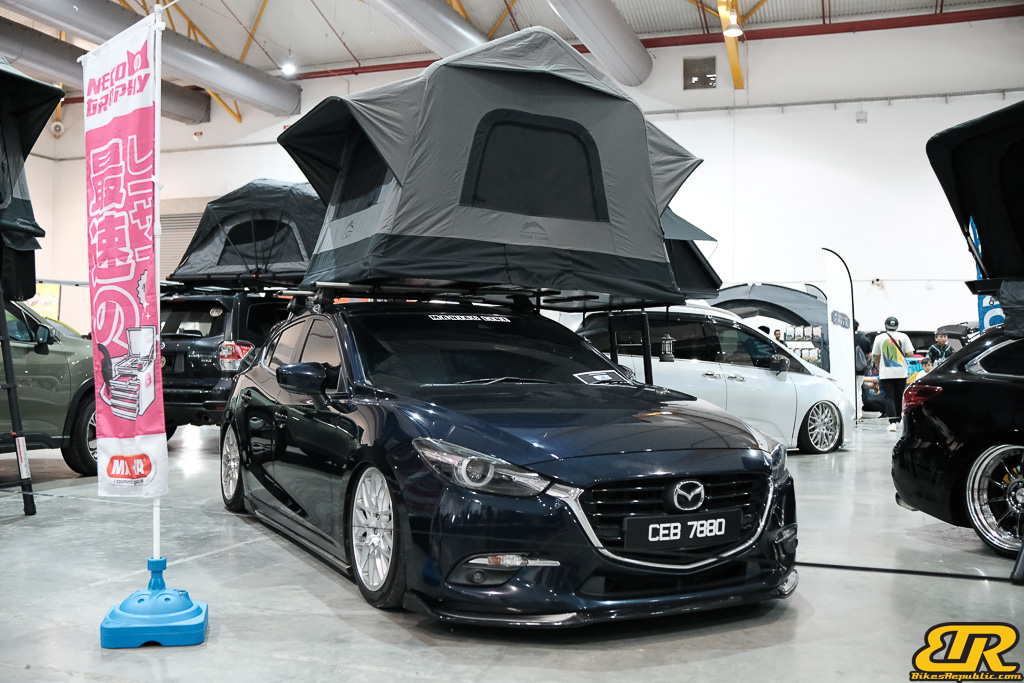
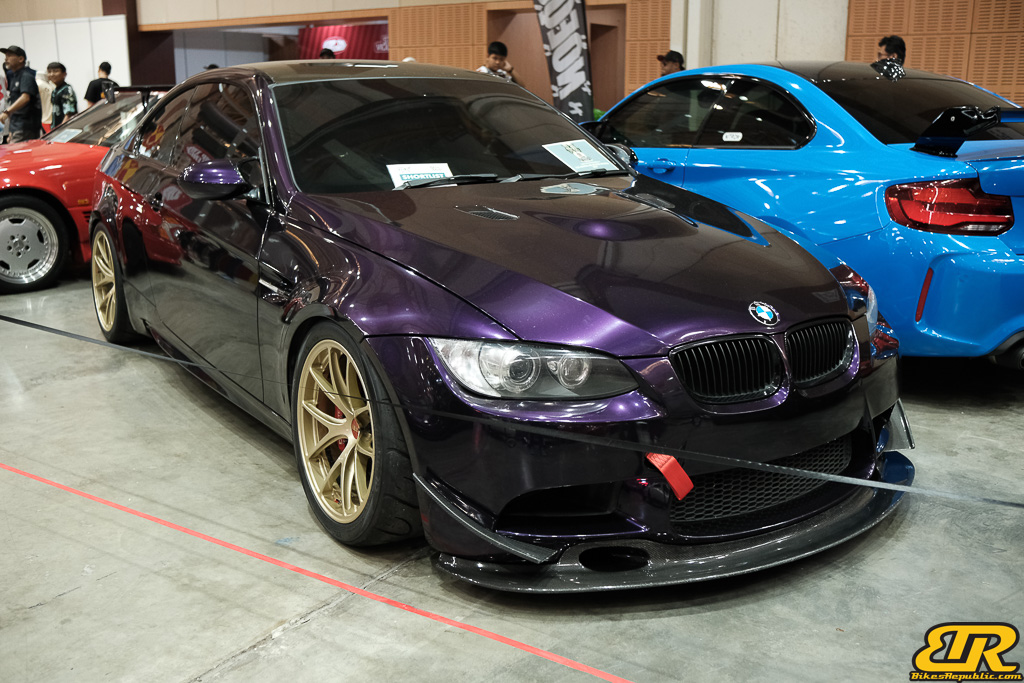
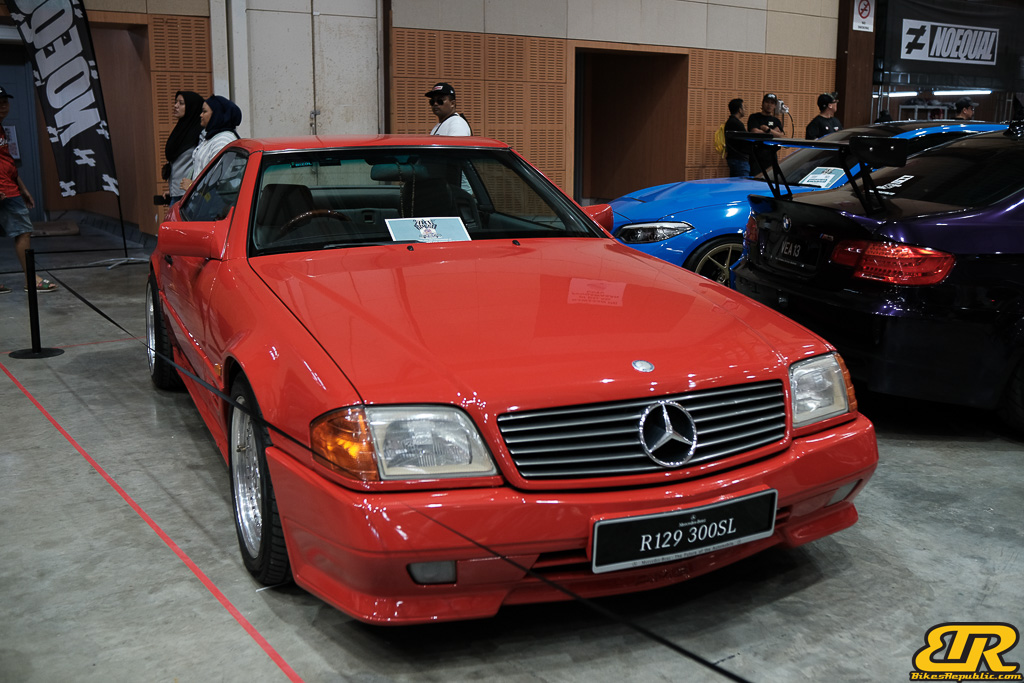
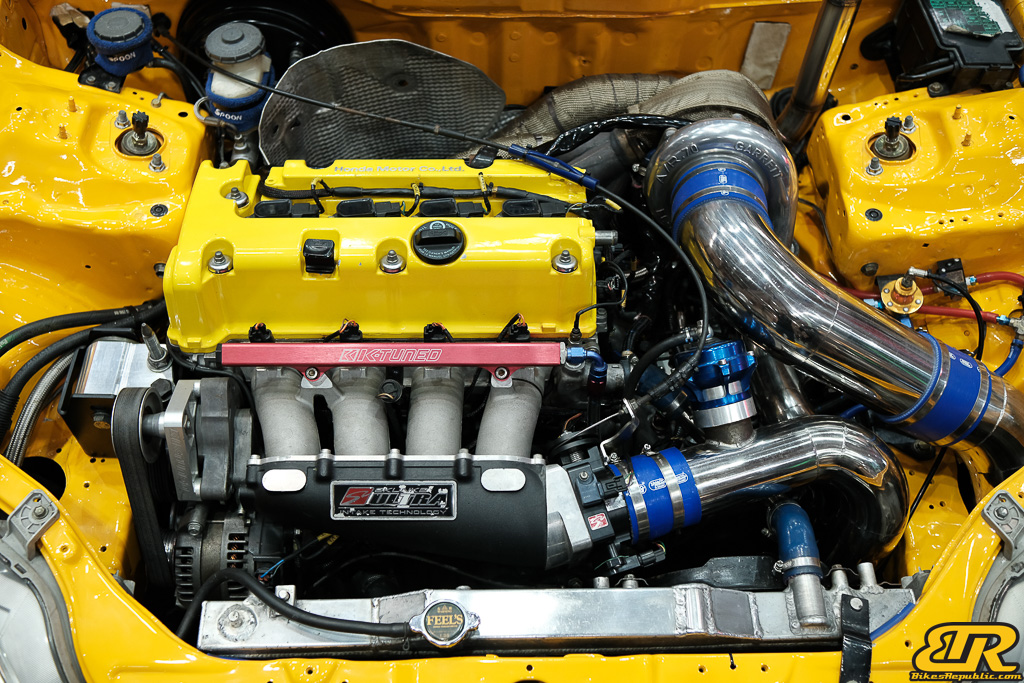
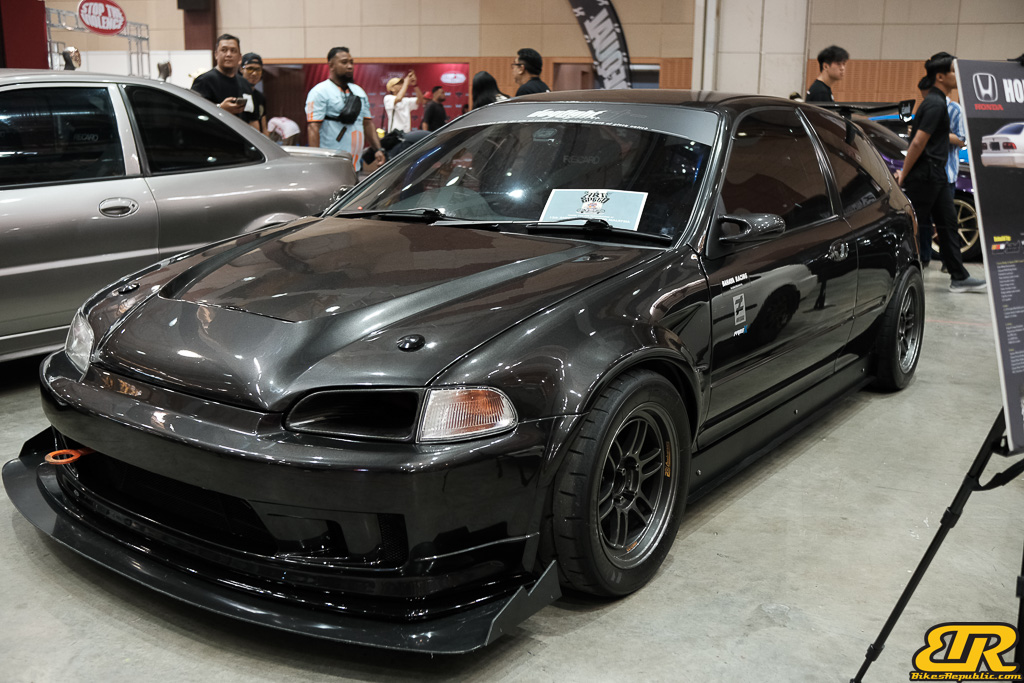
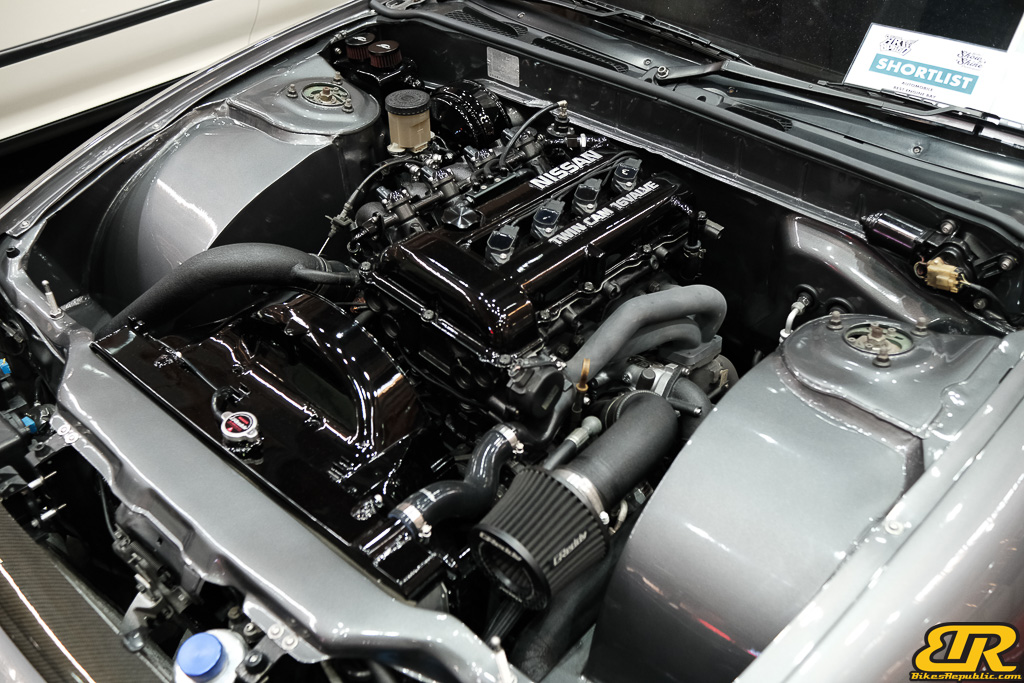
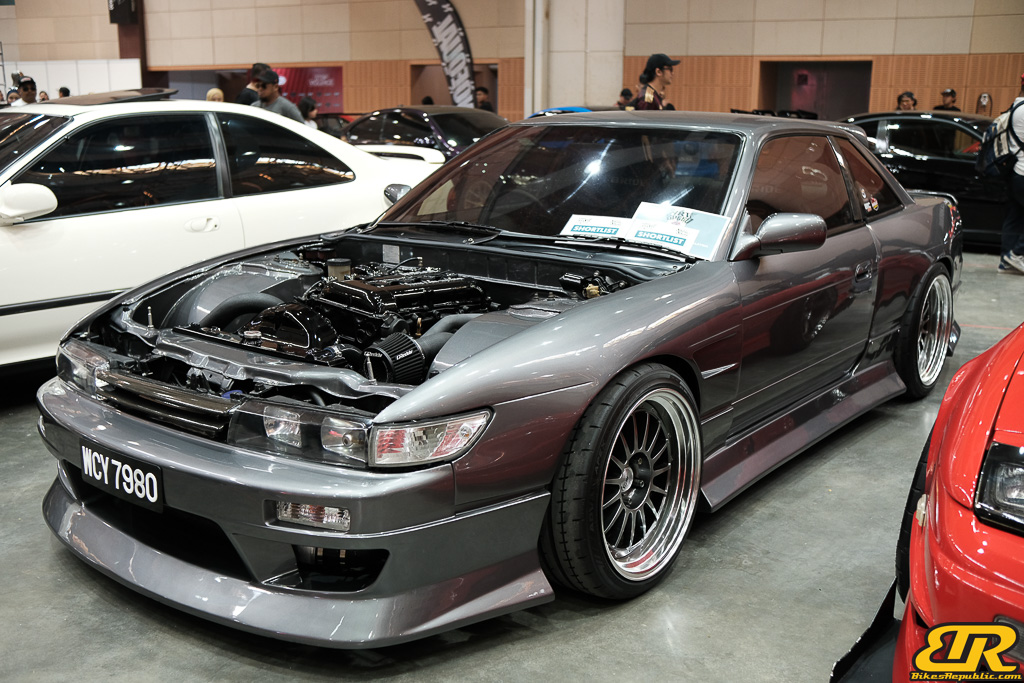
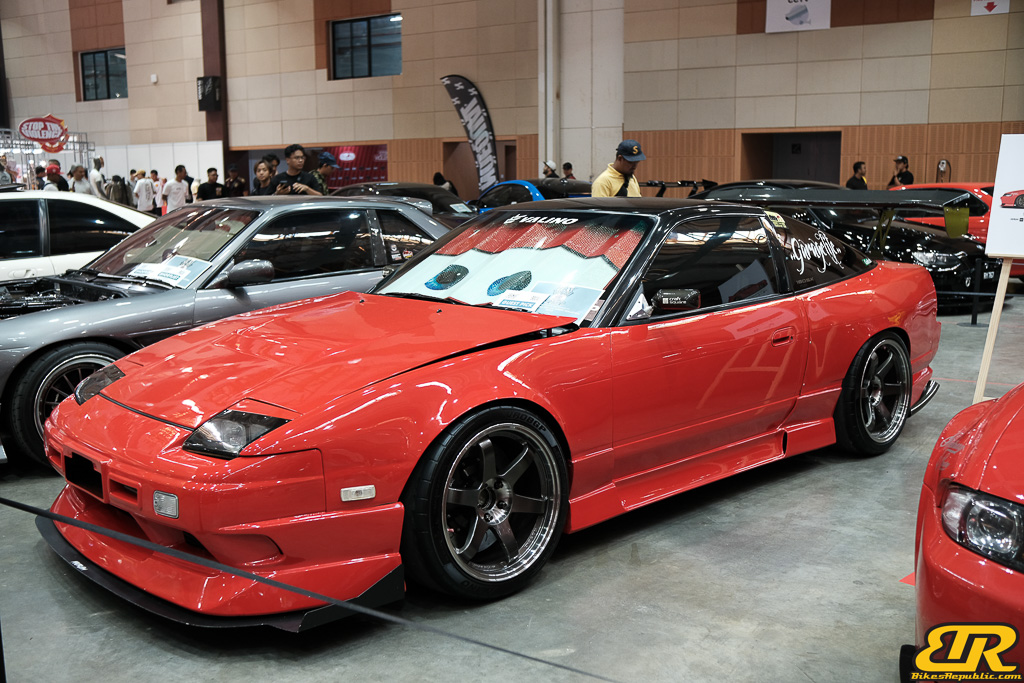
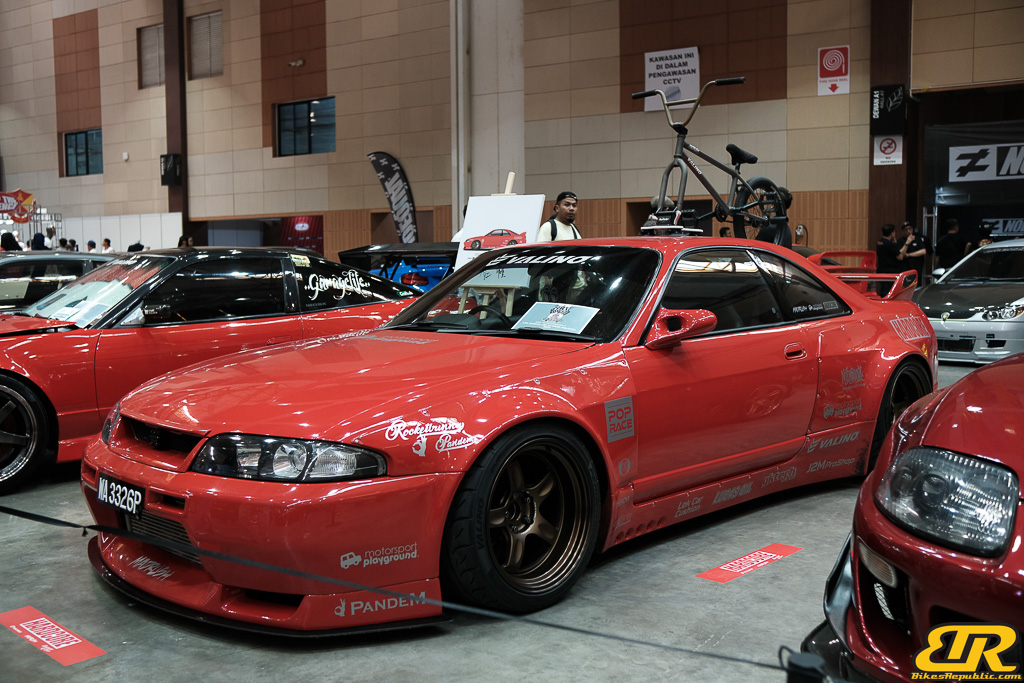
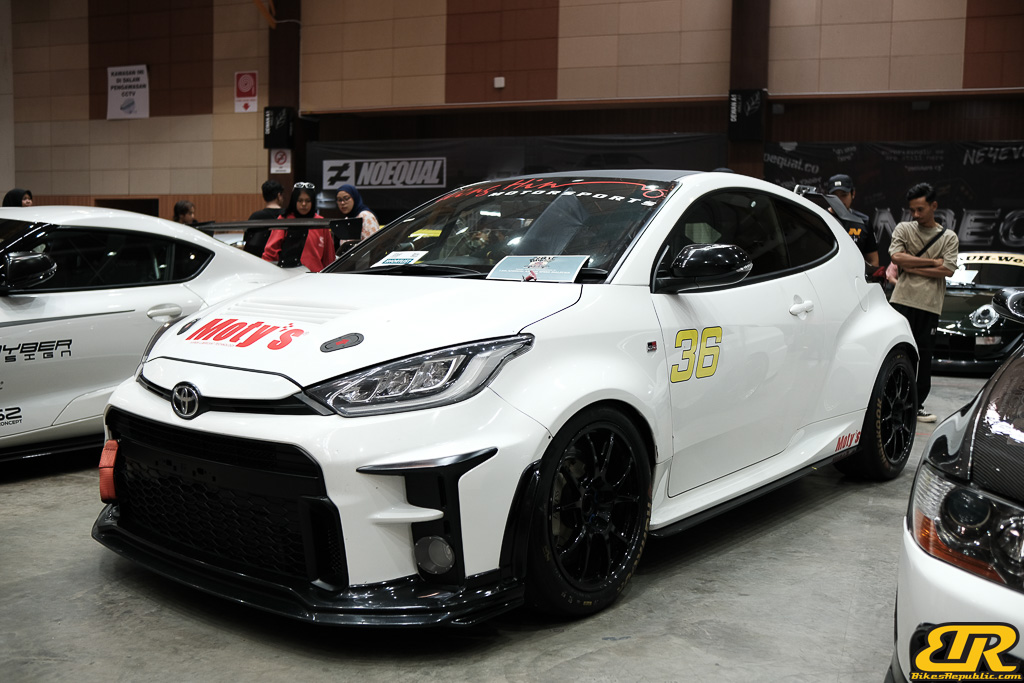
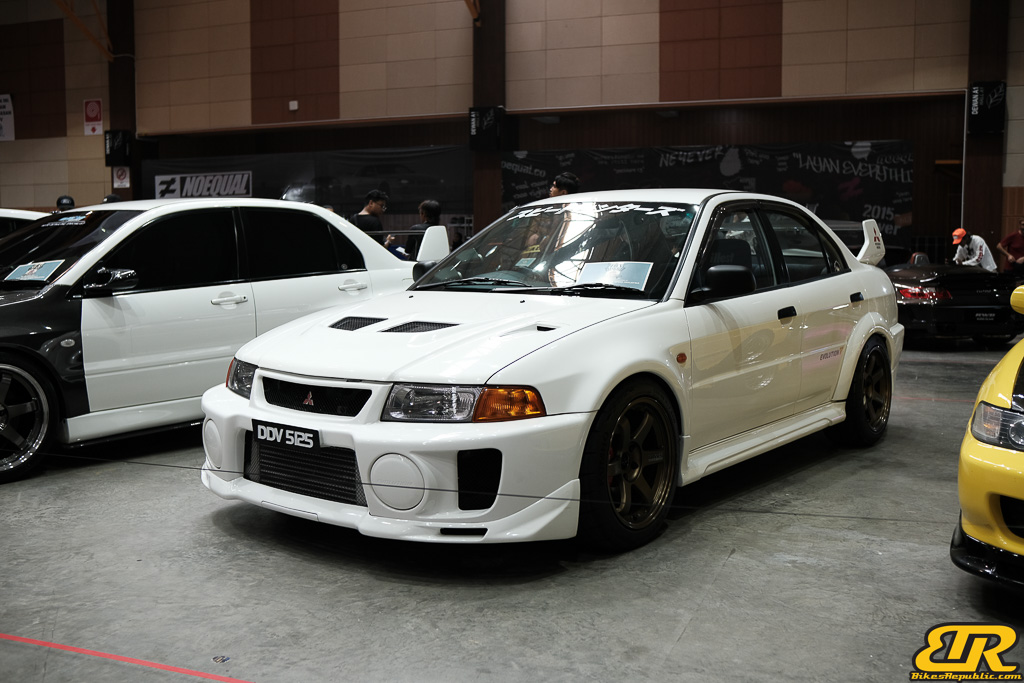
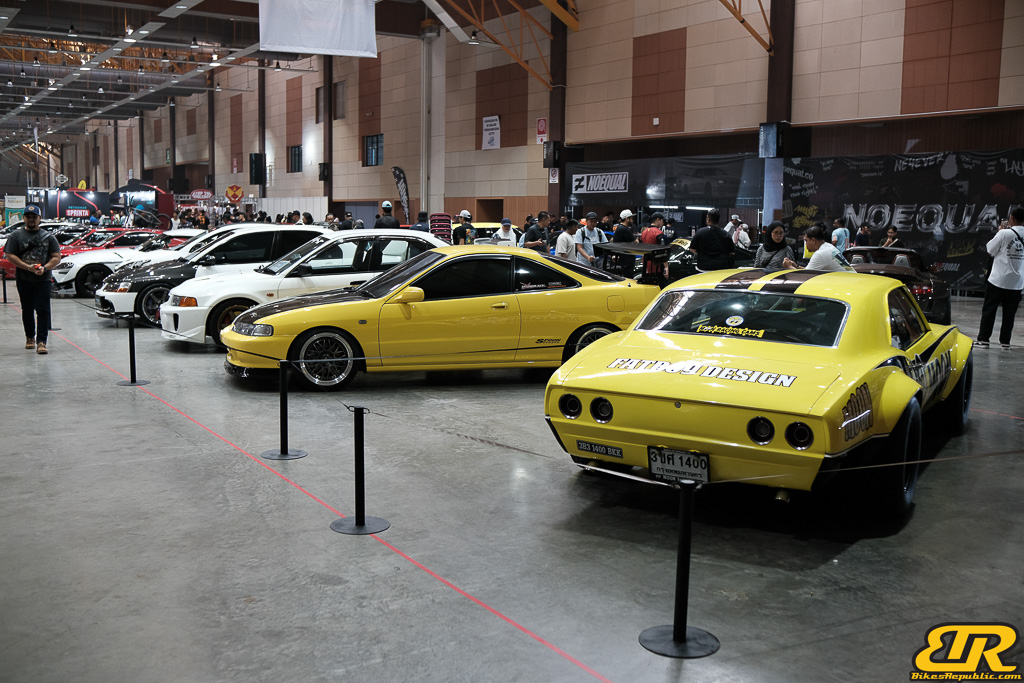
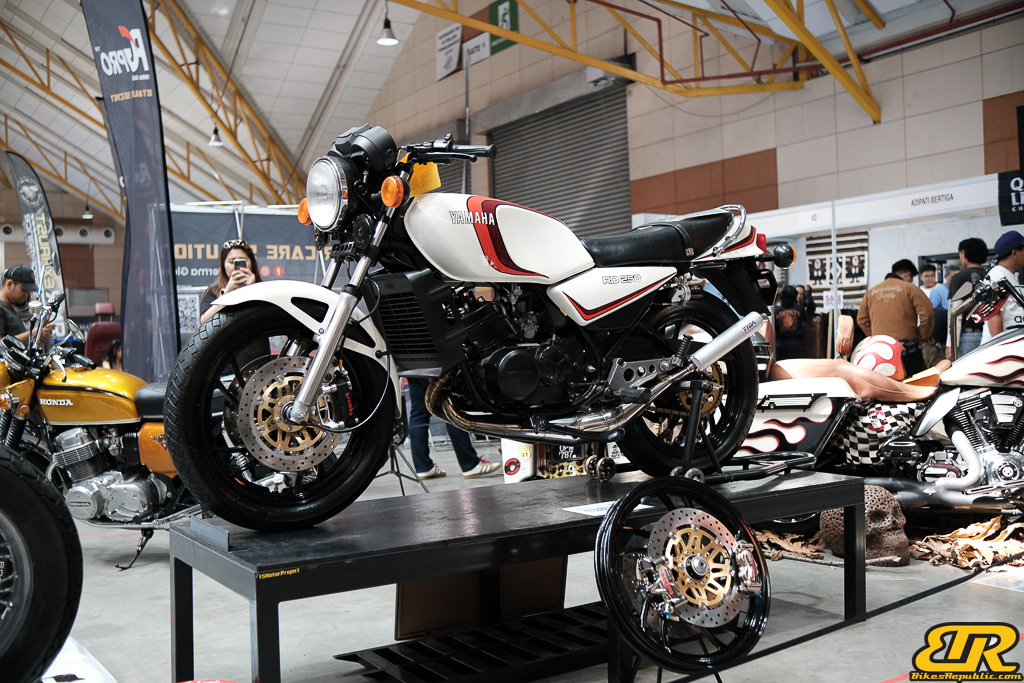
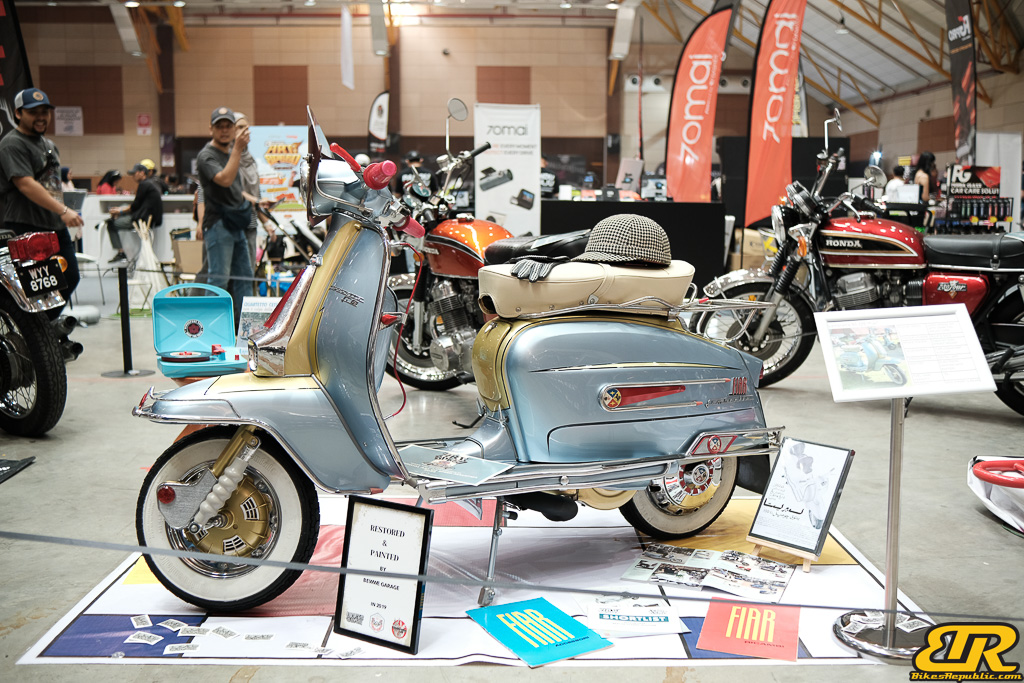
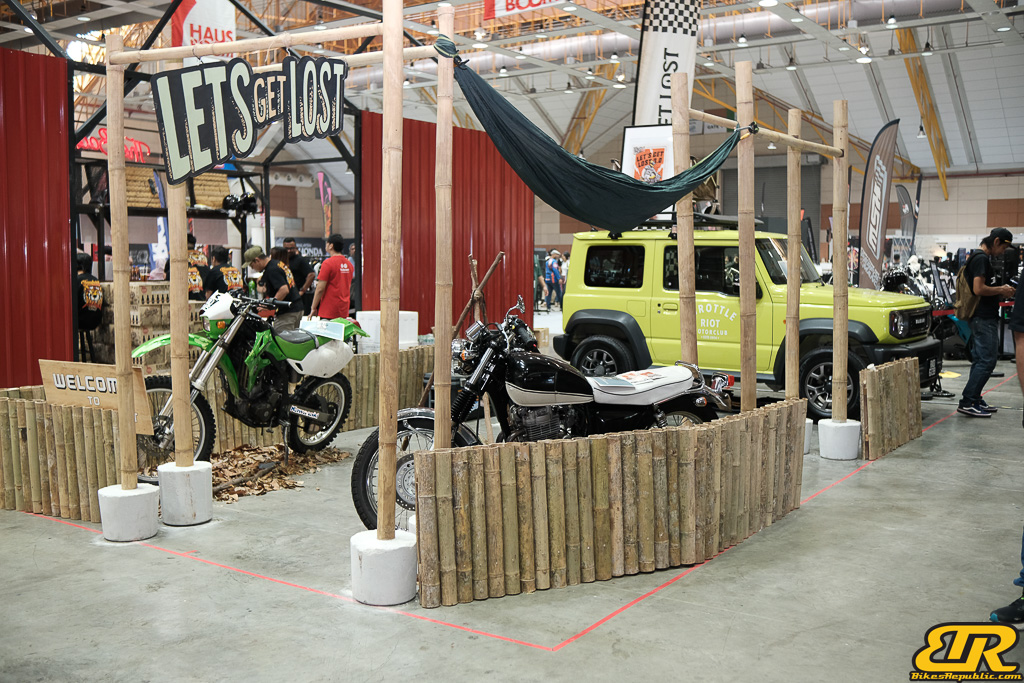
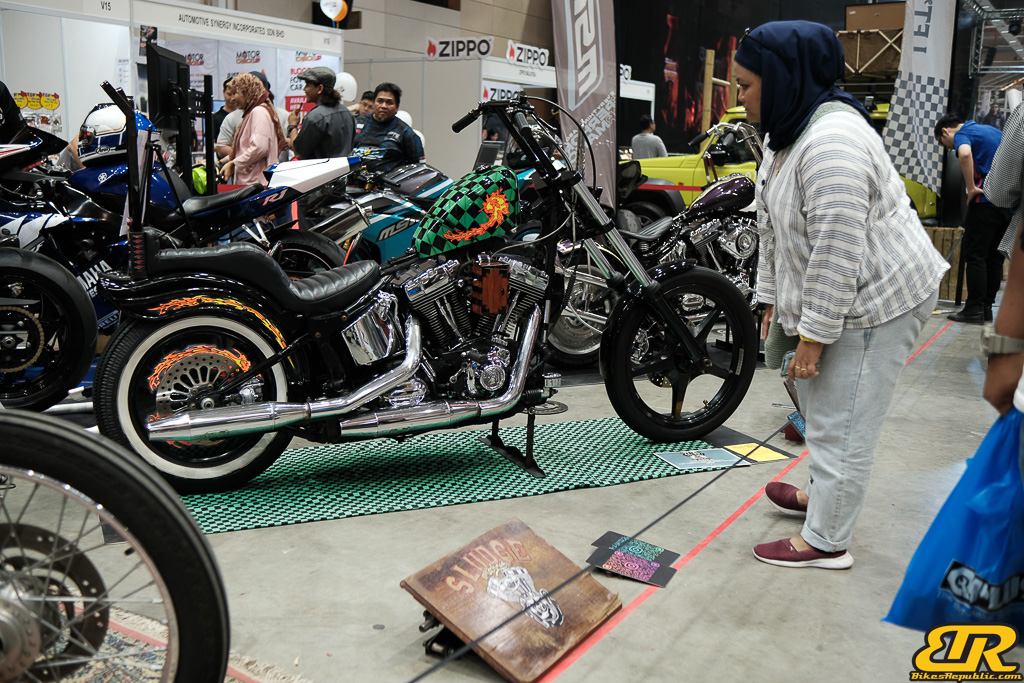
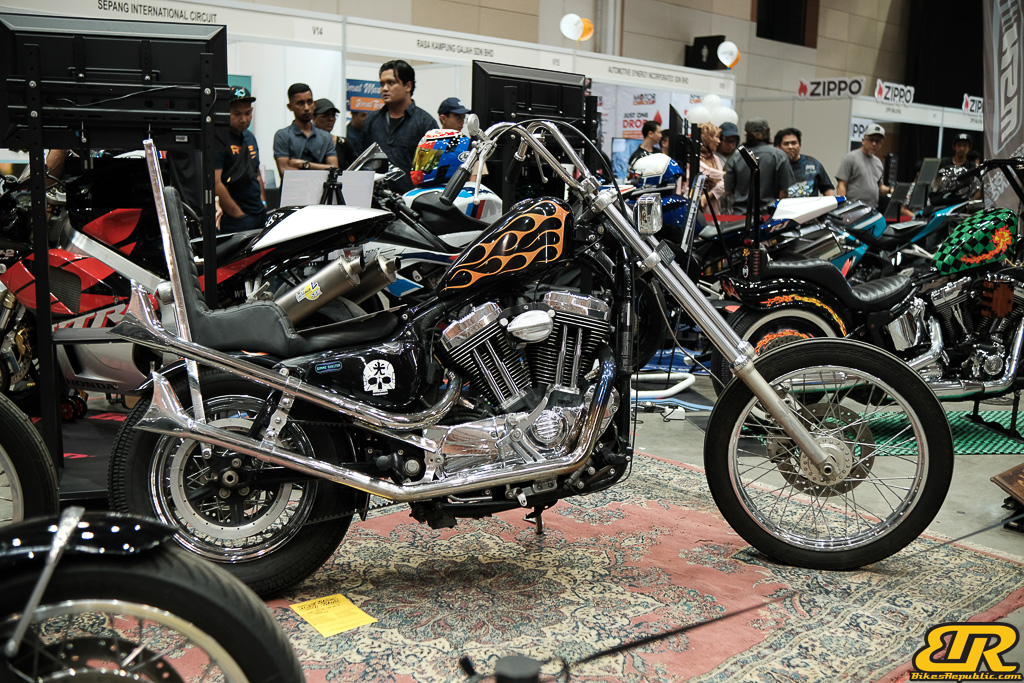
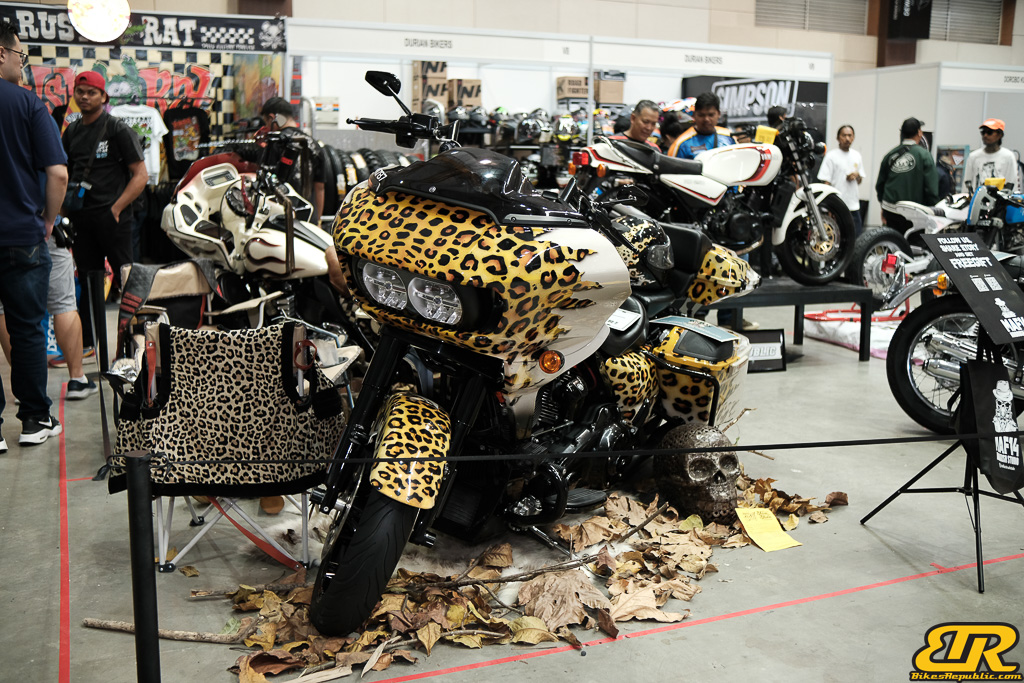
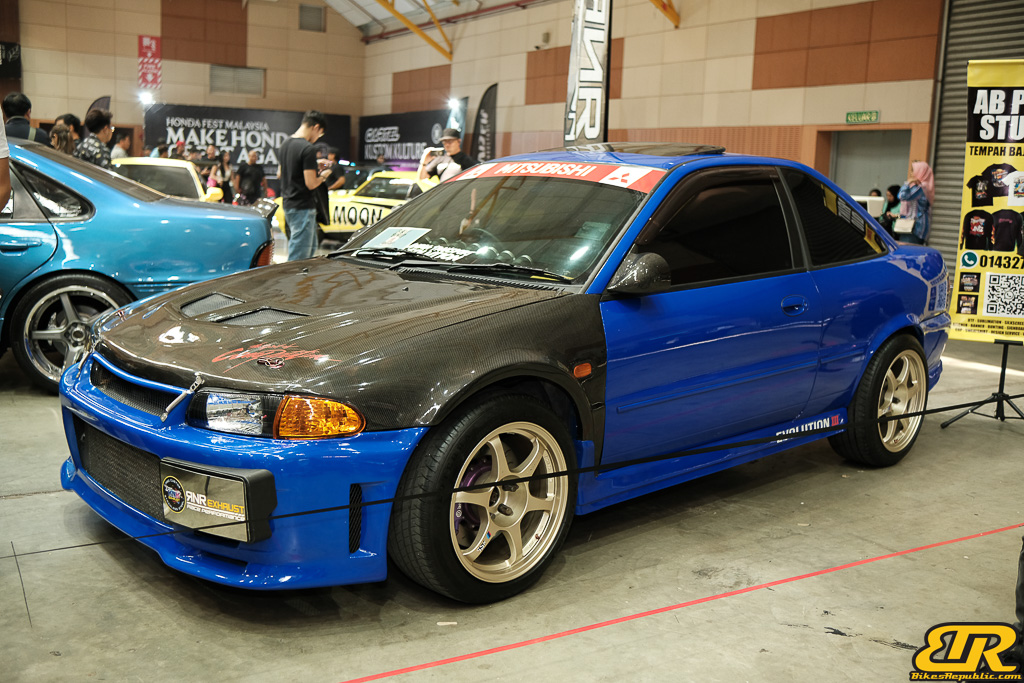
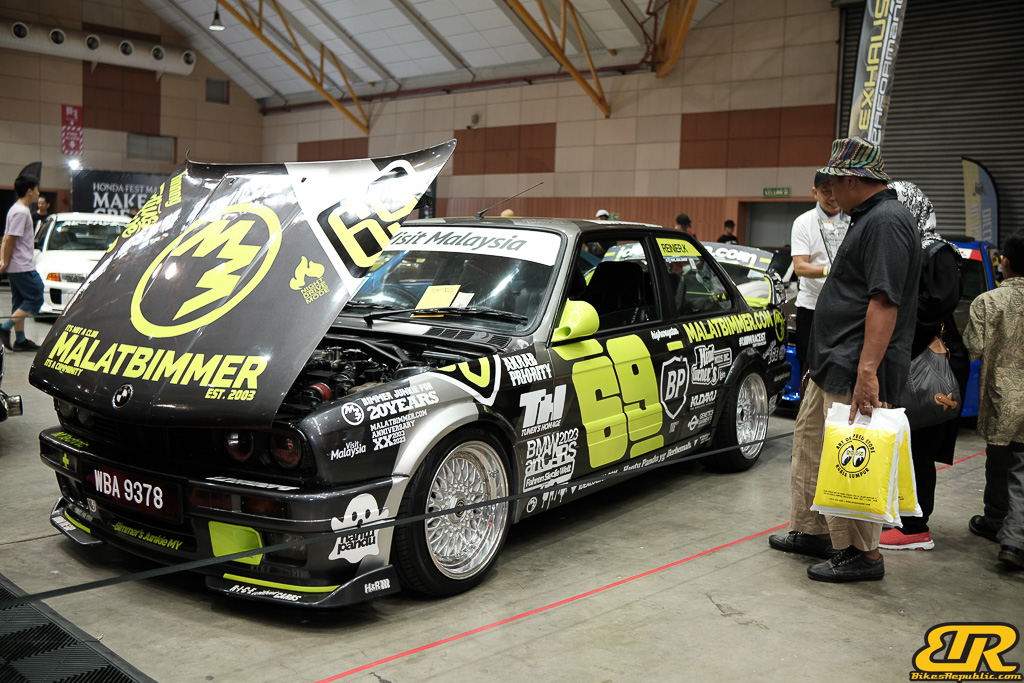
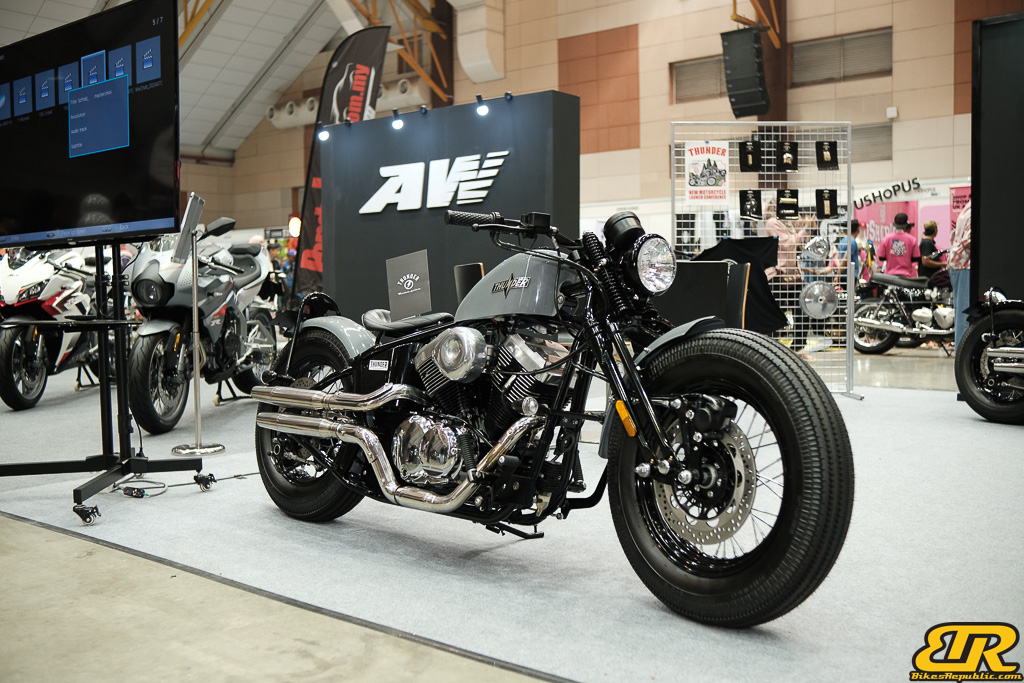
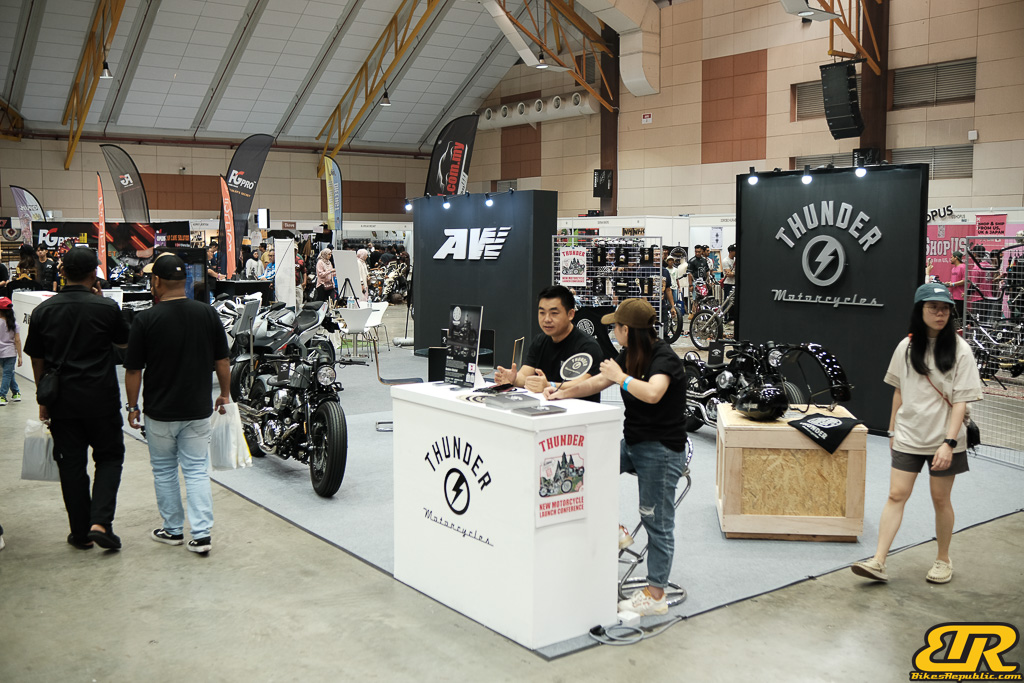
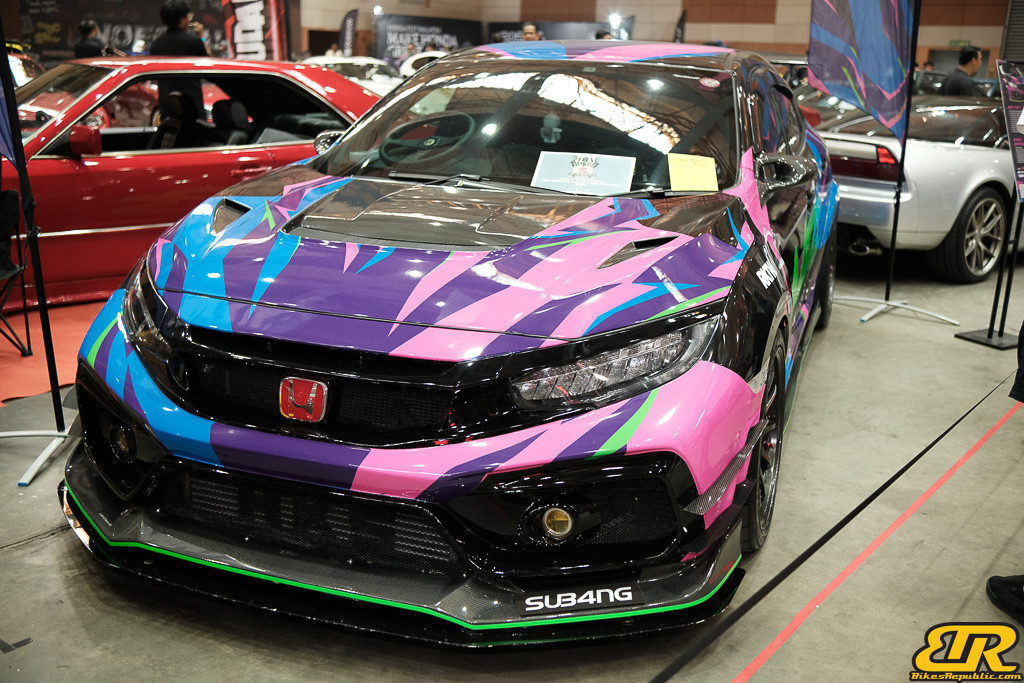
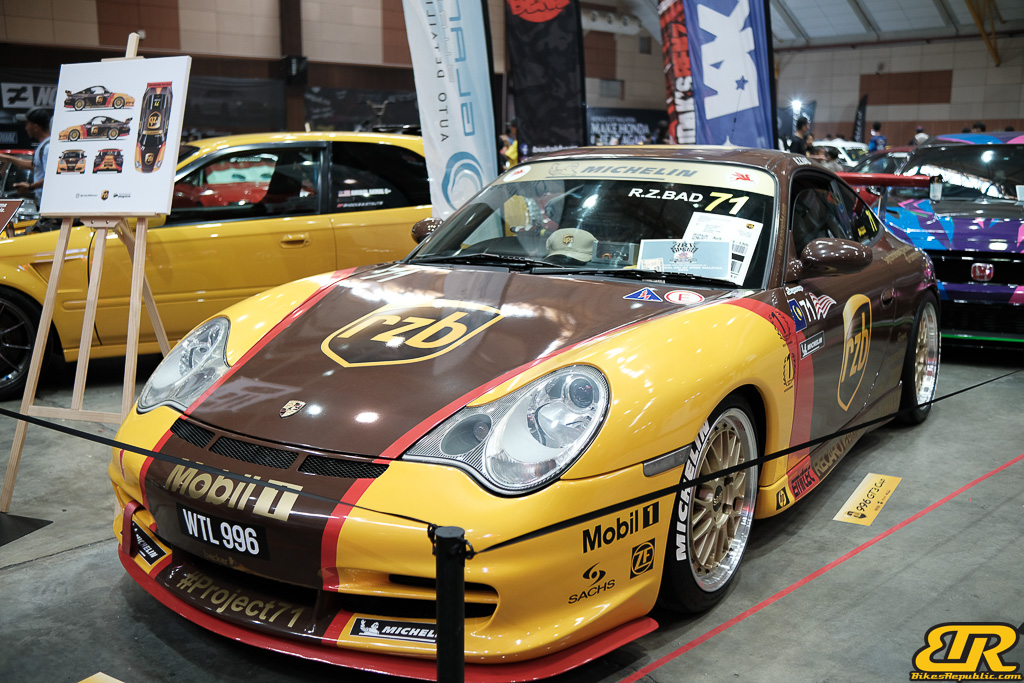
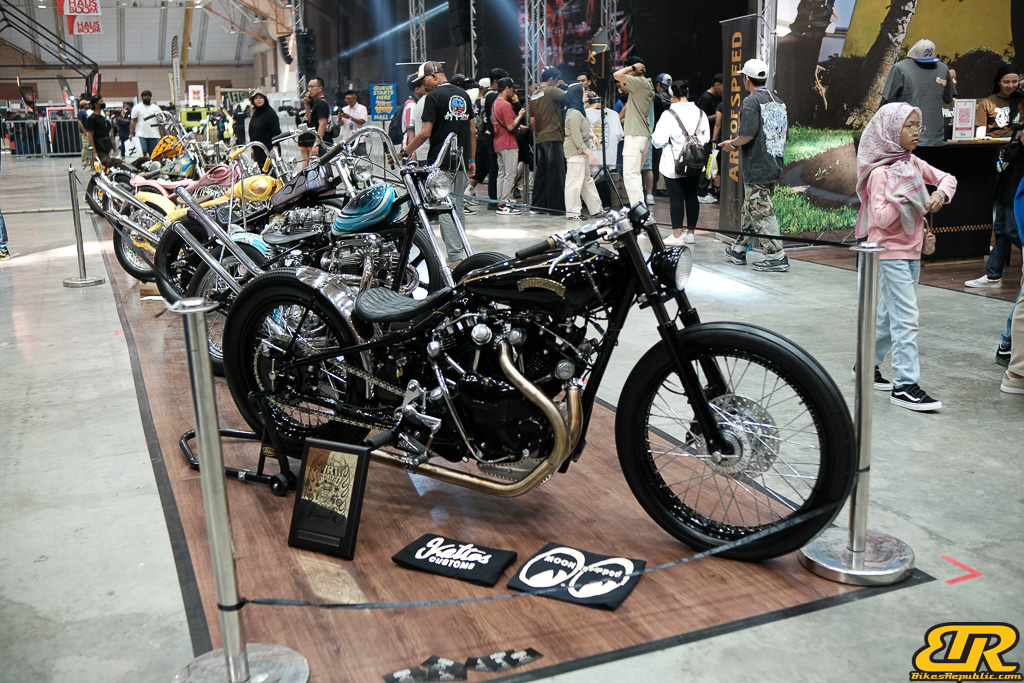
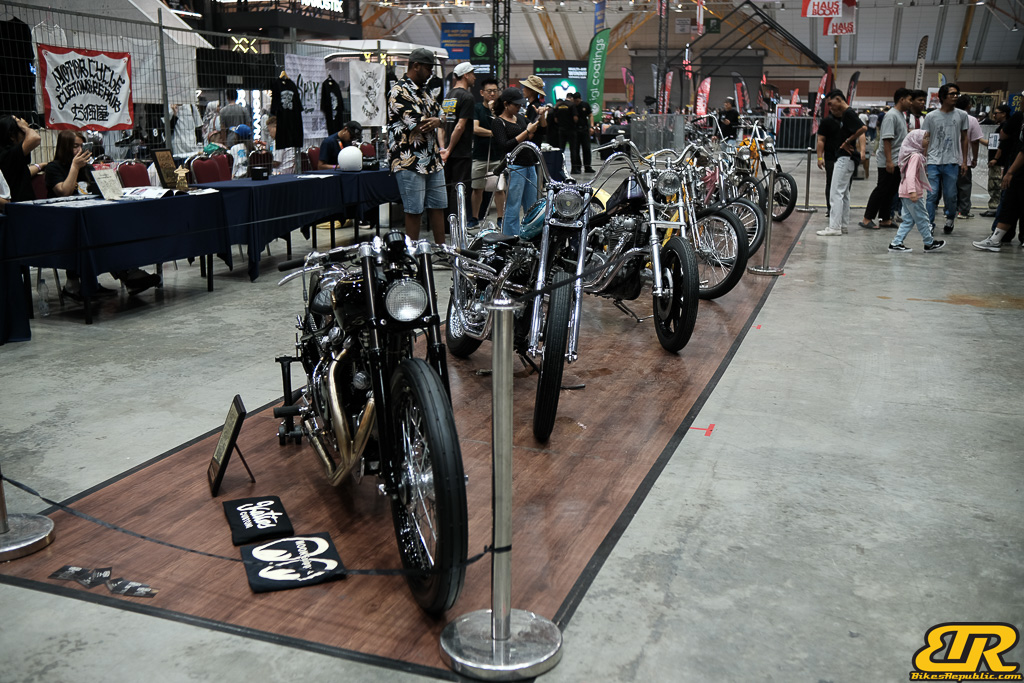
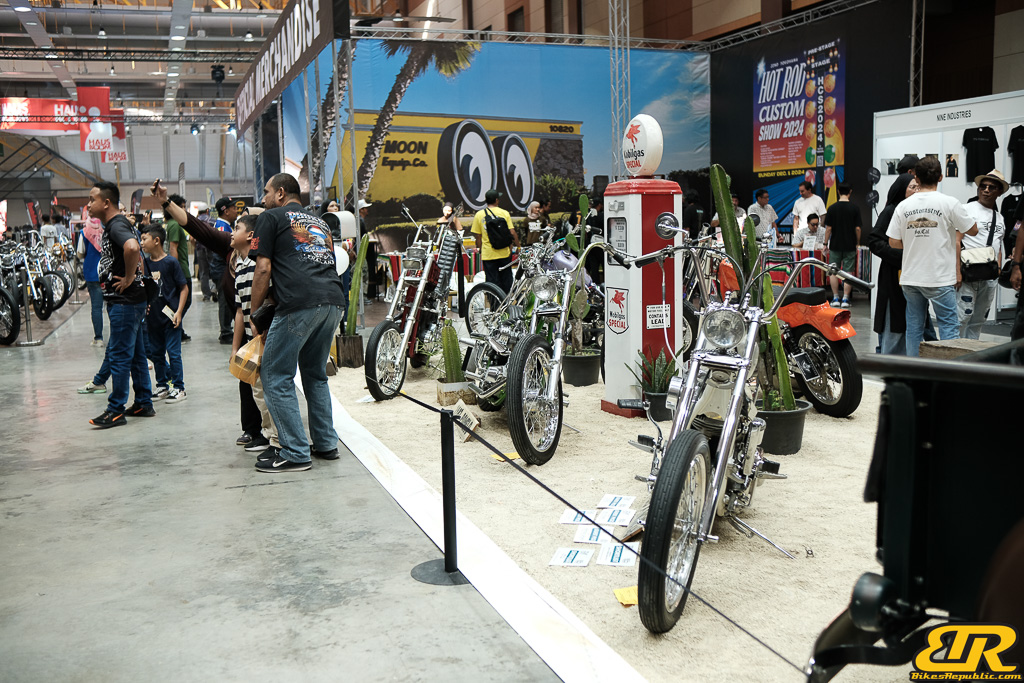
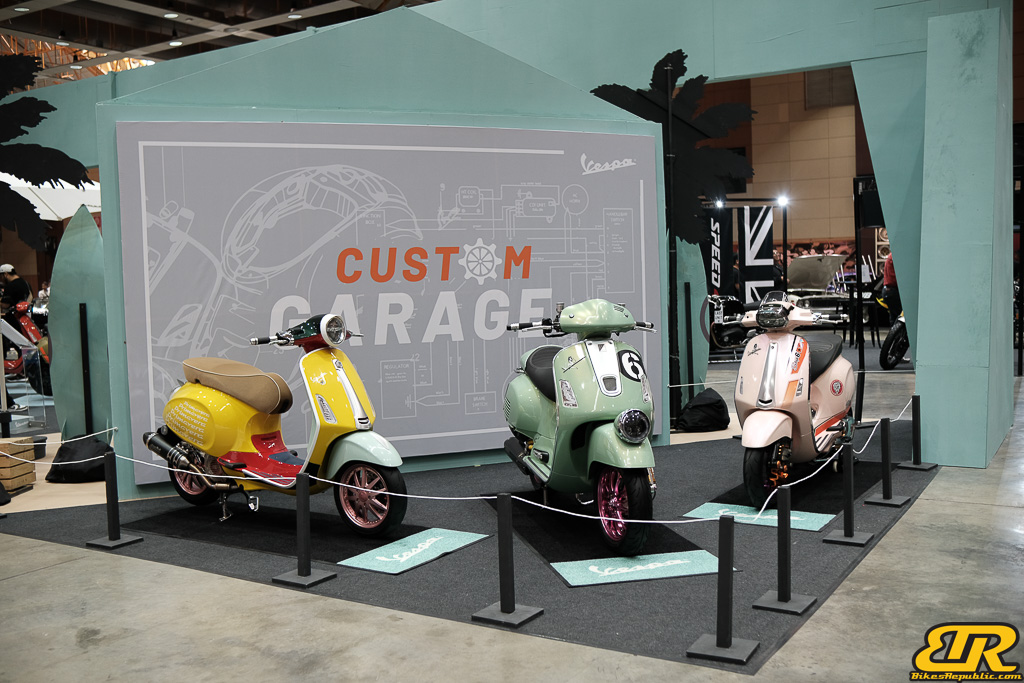
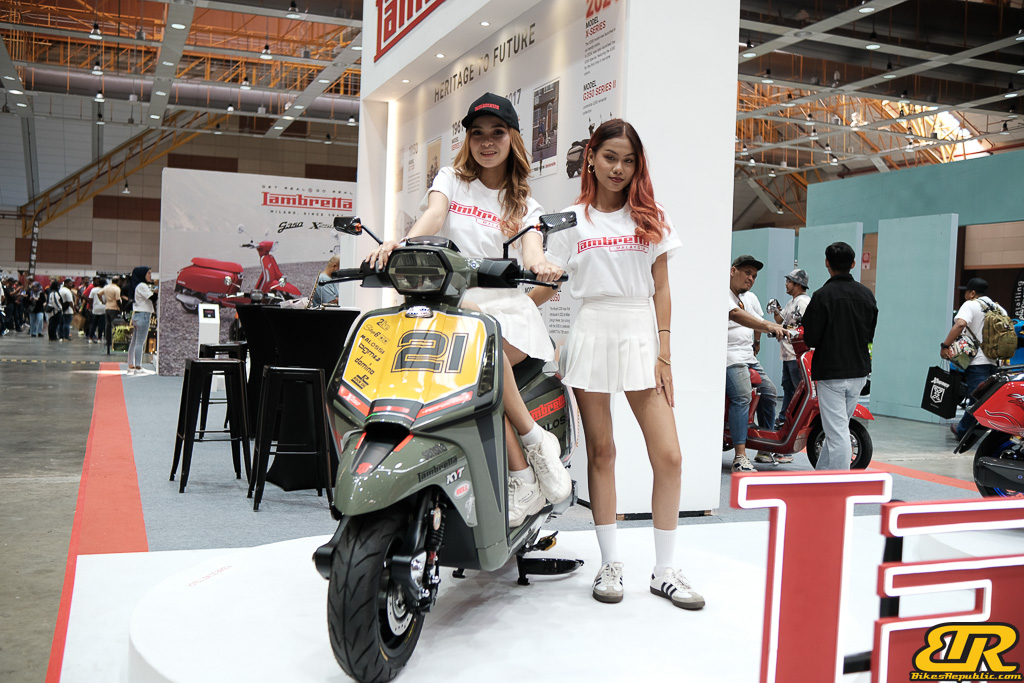
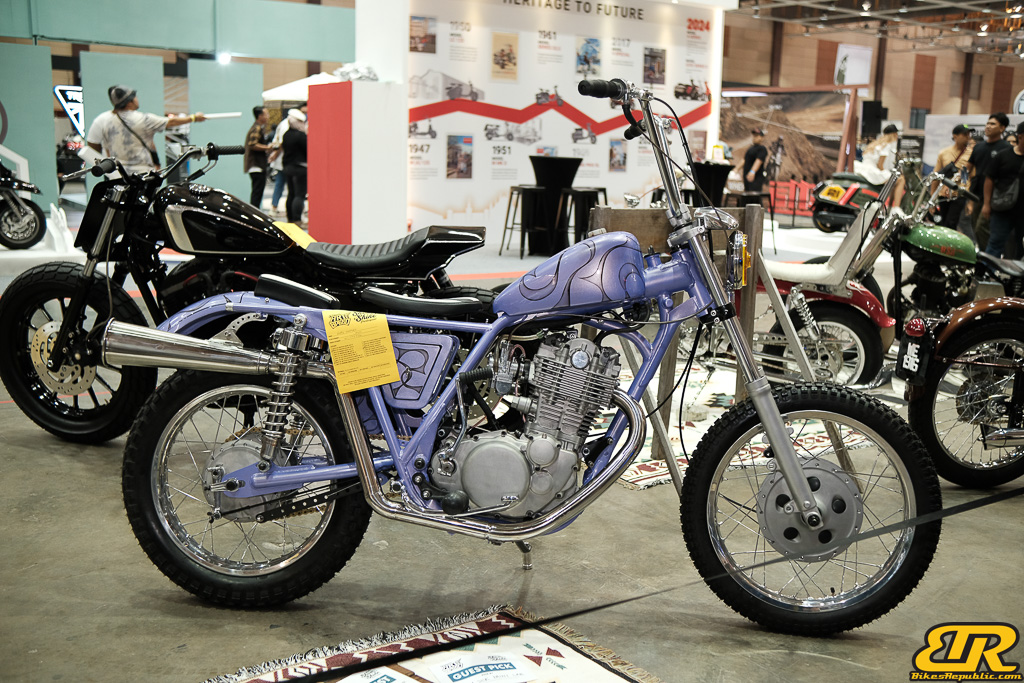
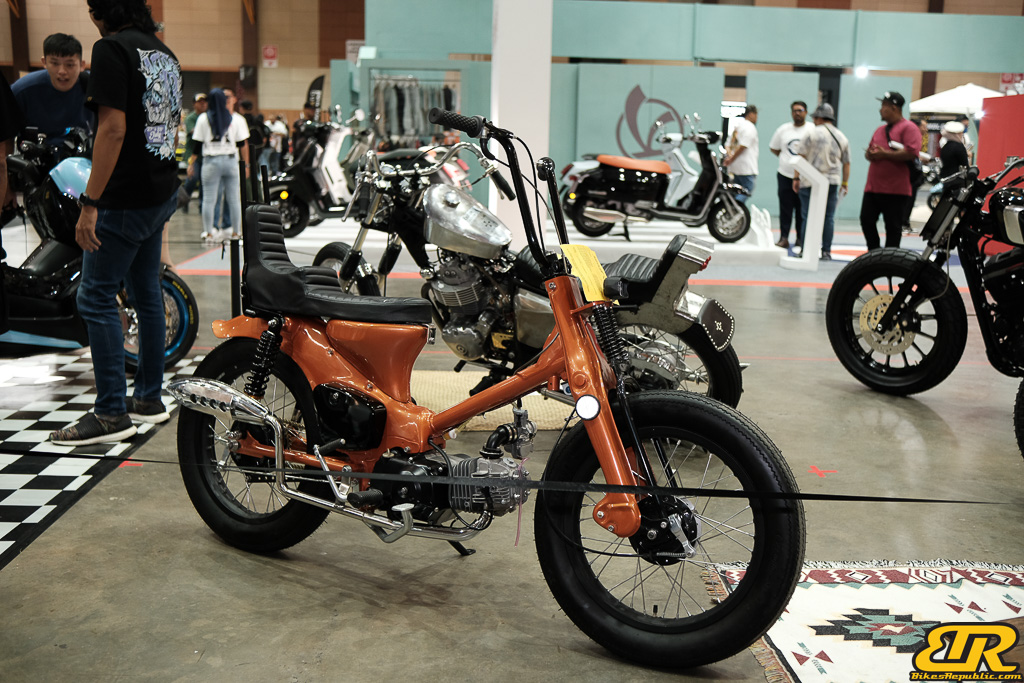
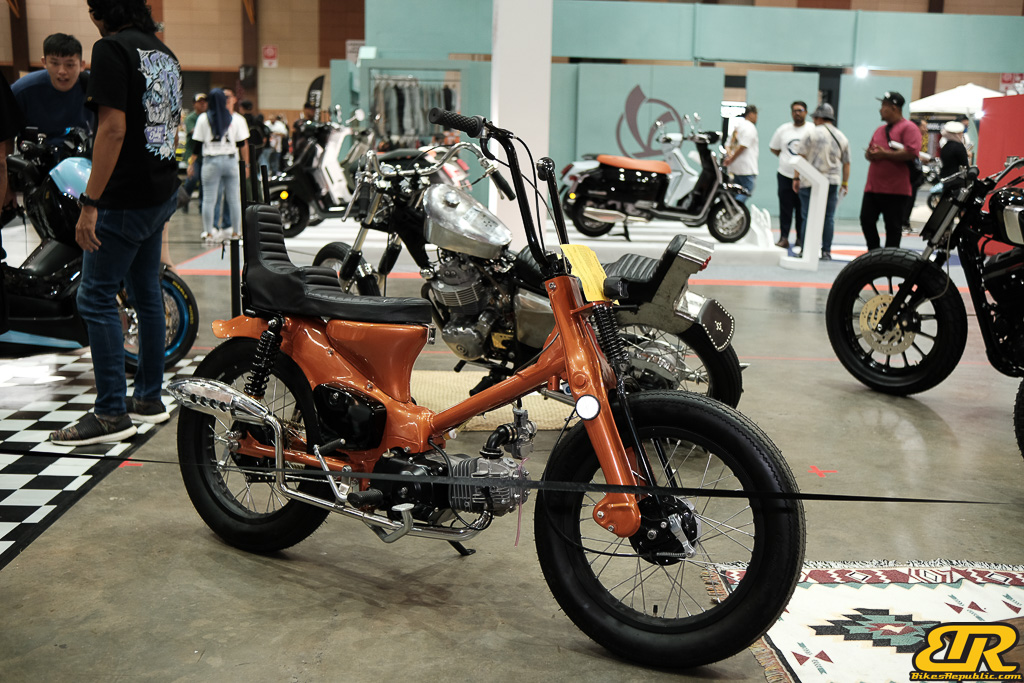
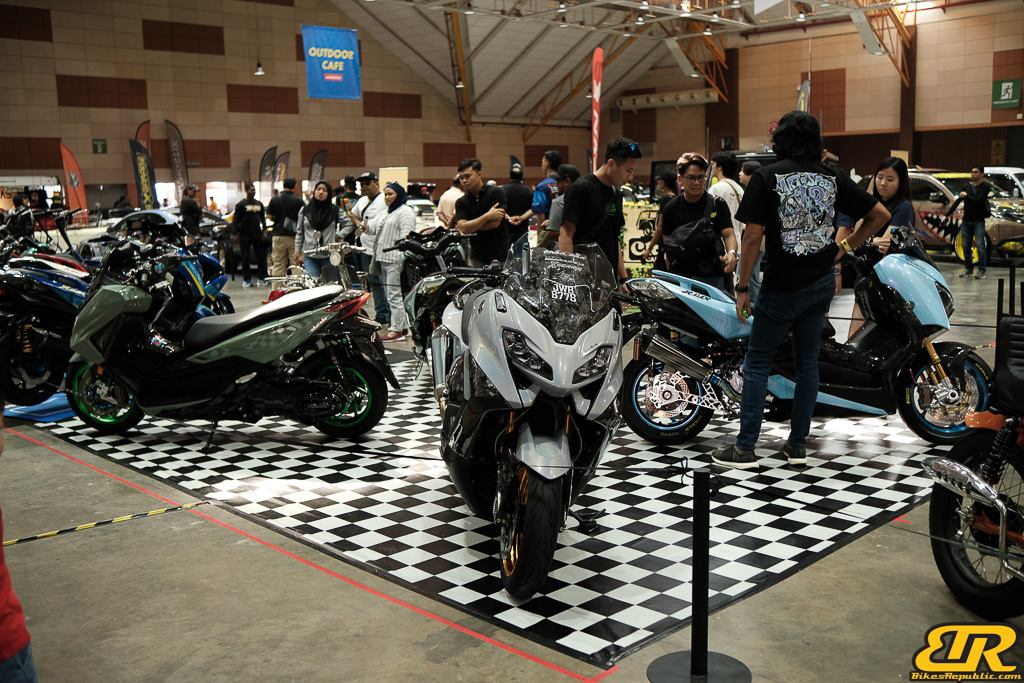
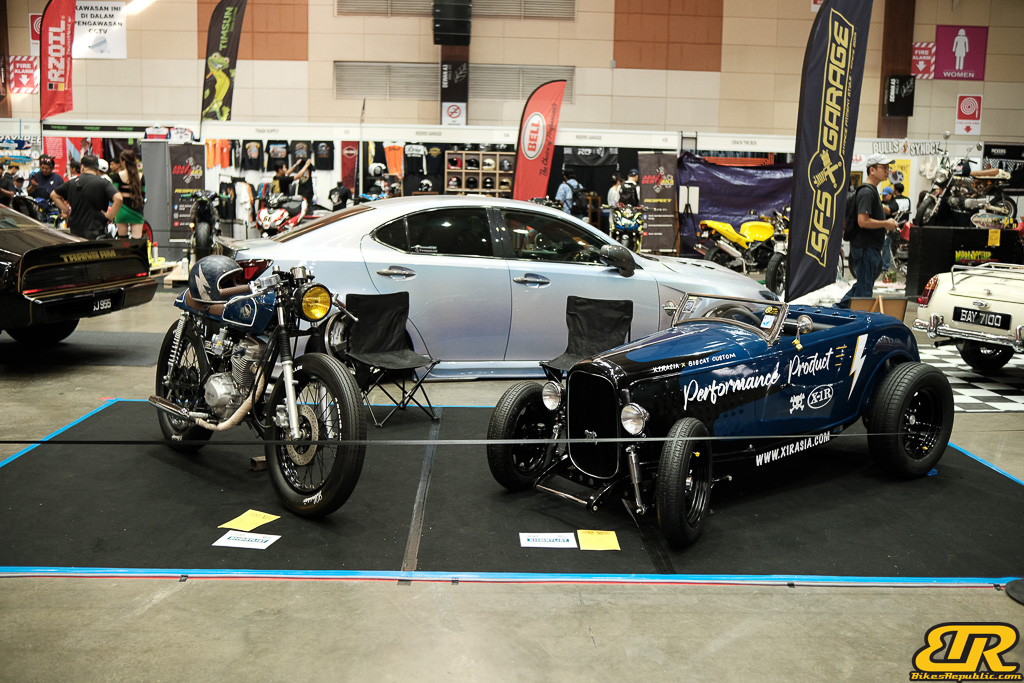
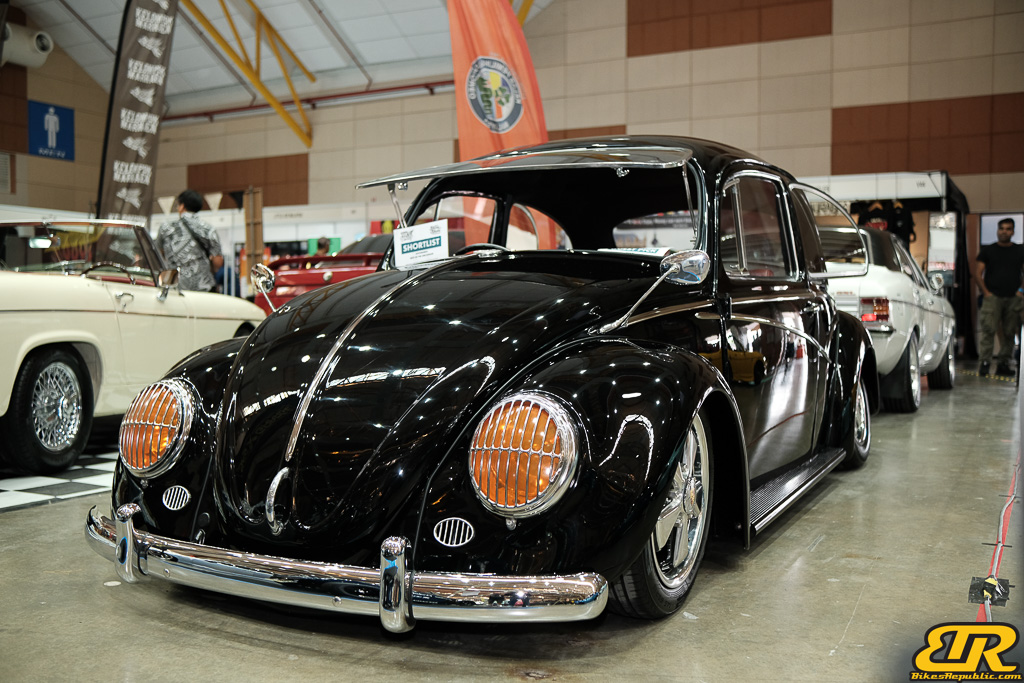
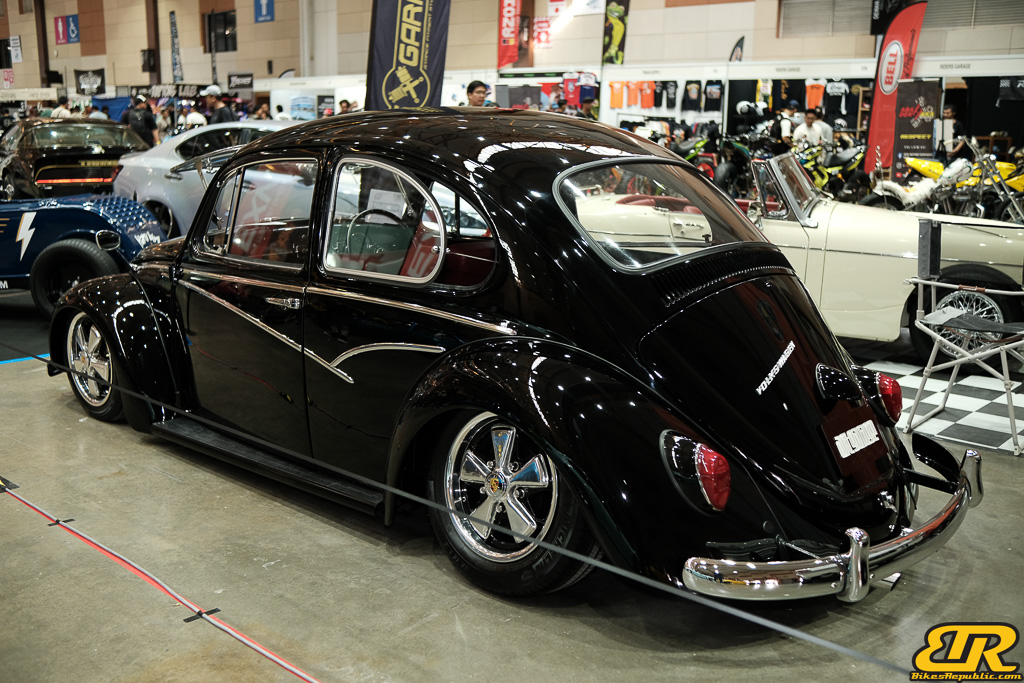
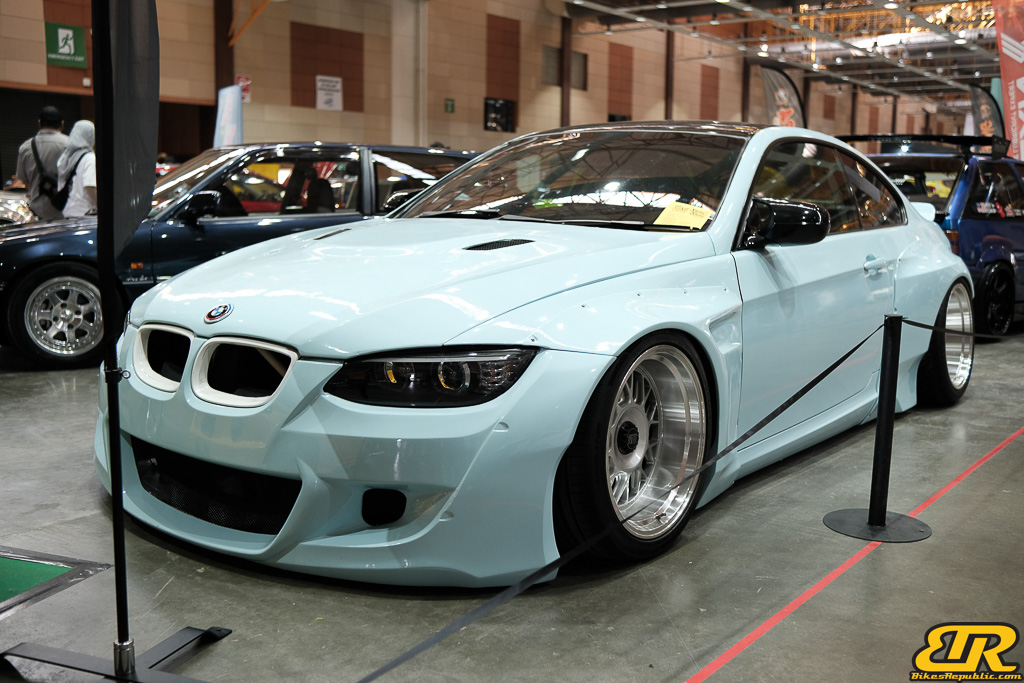
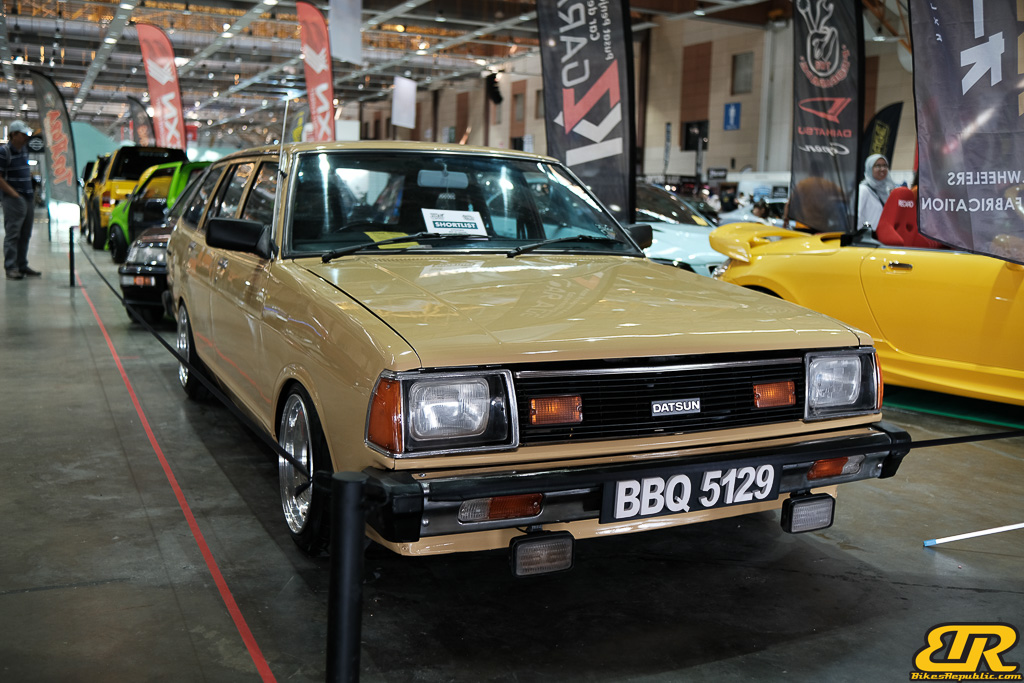
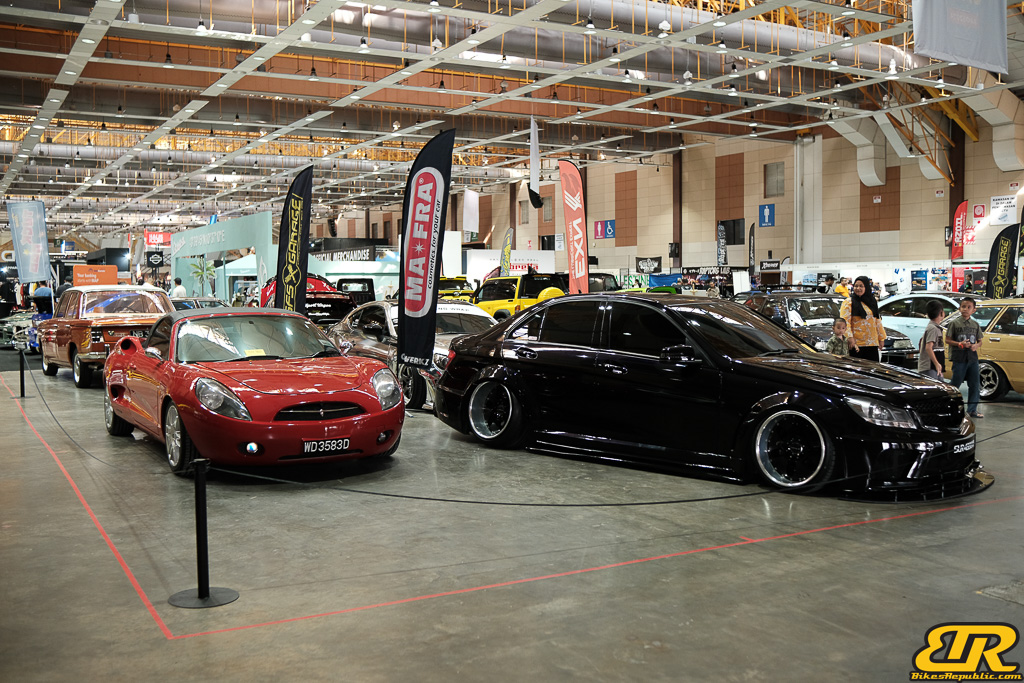
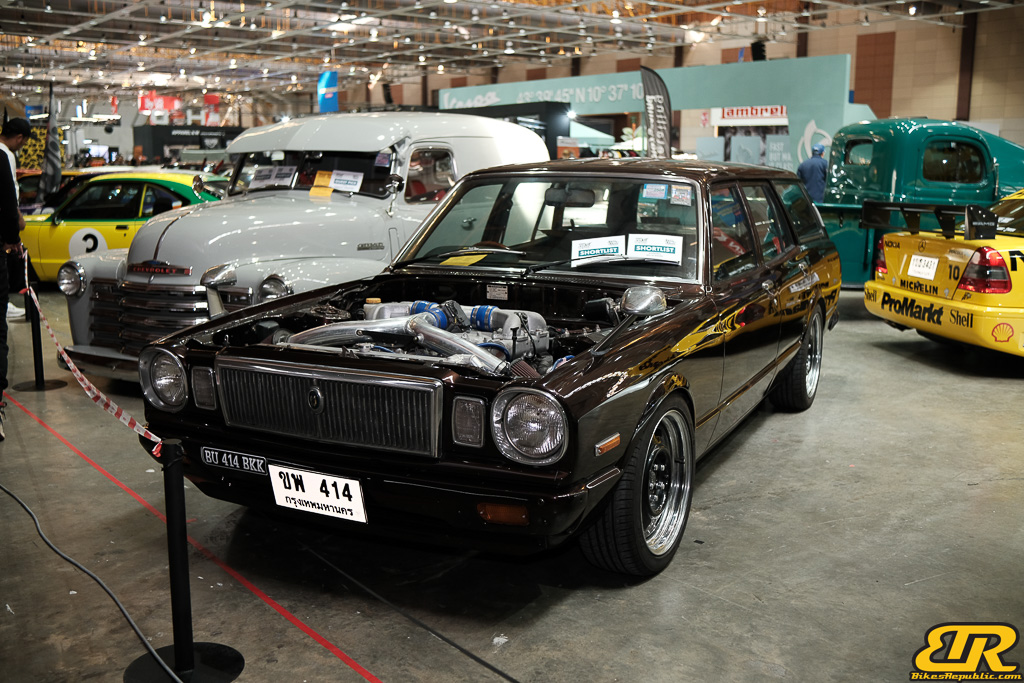
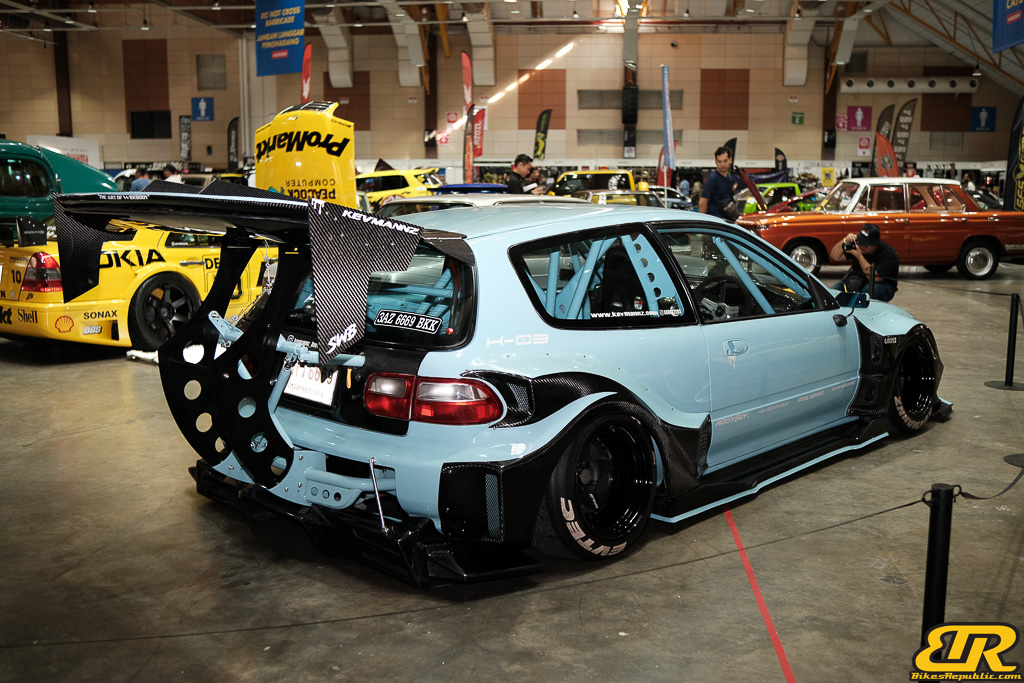
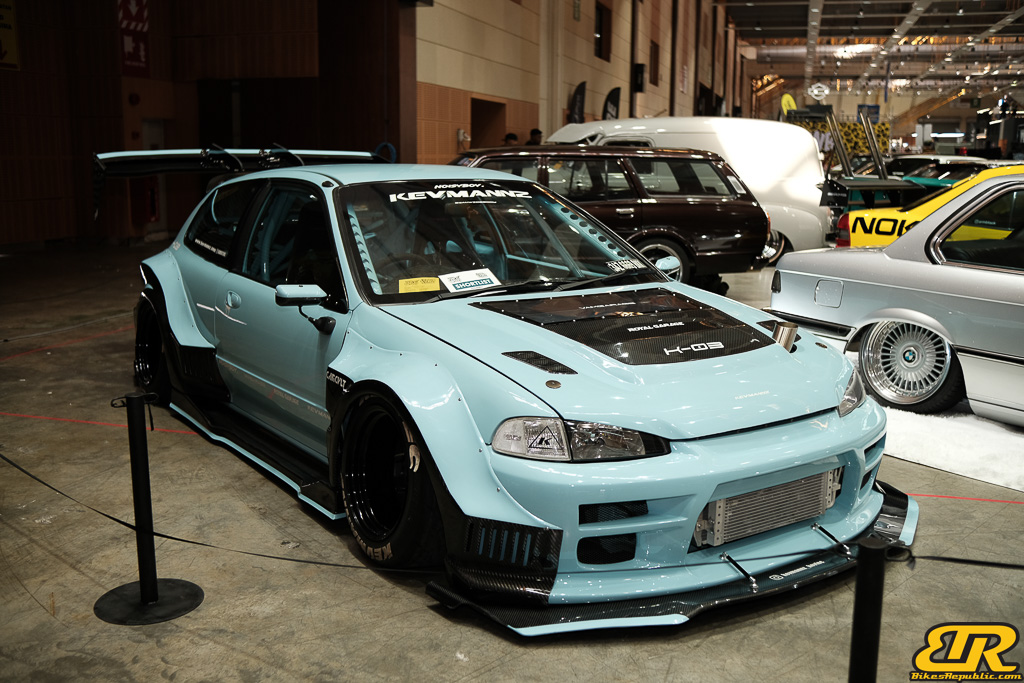
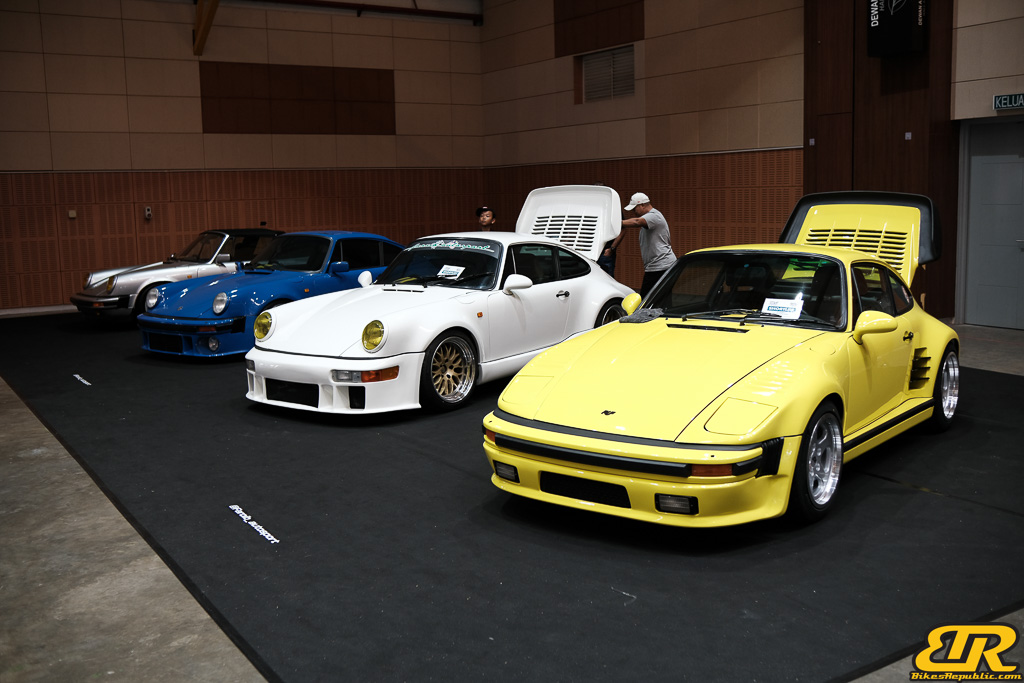
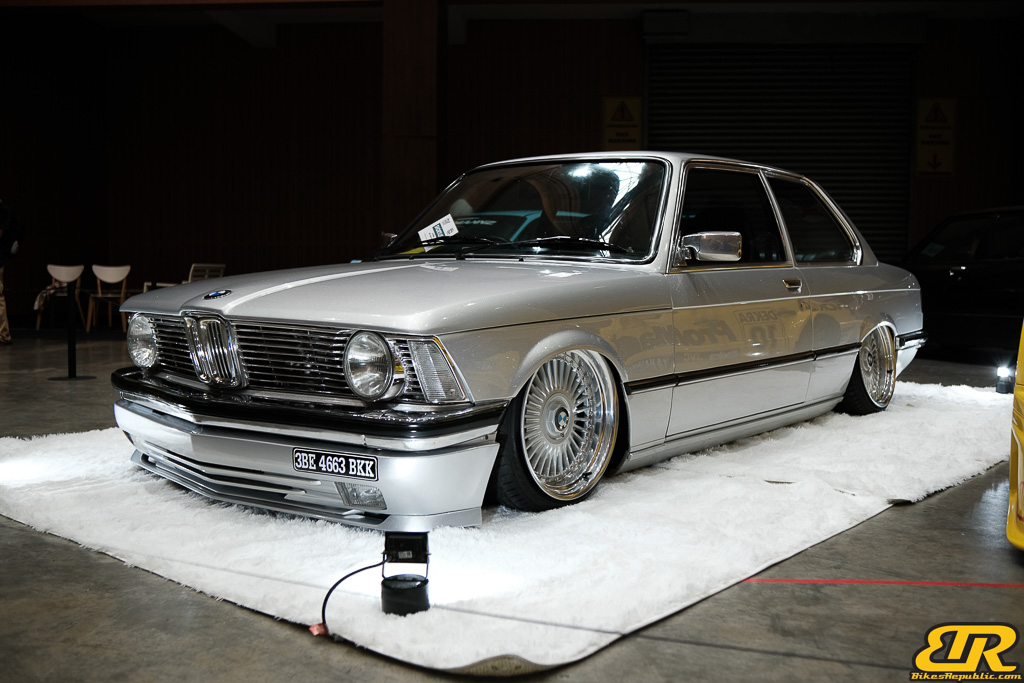
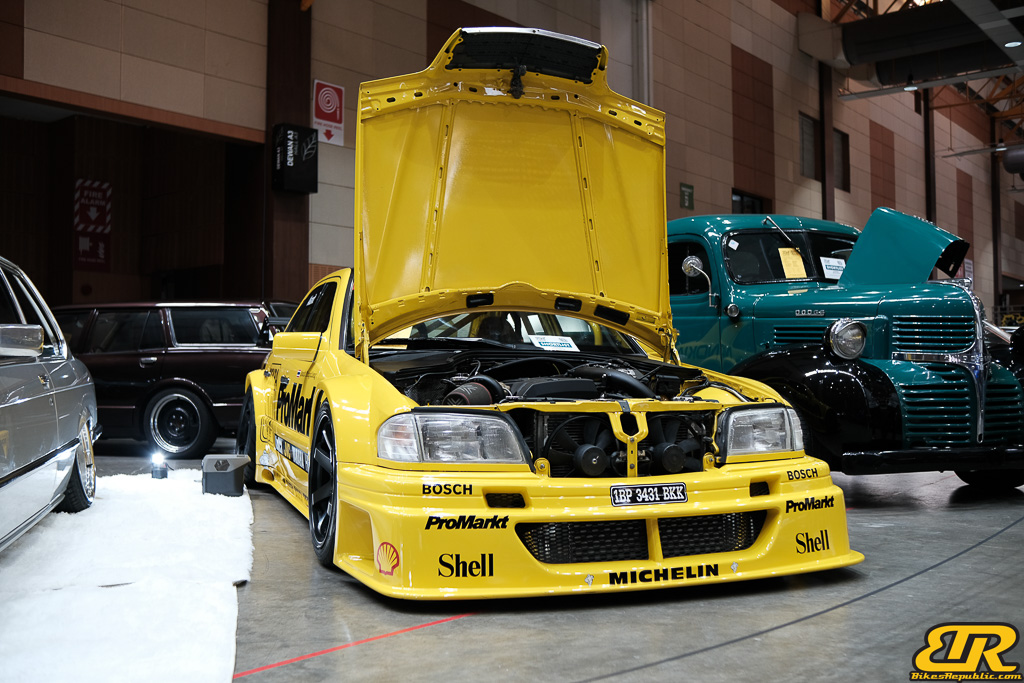
The 13th Annual Art Of Speed 2024 (AOS 2024) was held at the Malaysia Agro Exposition Park, Serdang (MAEPS) from 27 – 28 July 2024. And of course, it has grown from its humble beginning to the biggest and boldest motor show, regardless of its overall custom culture theme. And, it has gone fully international.
Begin press release:
Art Of Speed’s tradition of various international guests together with a showcase of customized vehicles from overseas has always been one of the main highlights that draws both visitors and fans alike.
This year’s distinguished guests include:
- Shige Suganuma, Shinotsuka “NATQQ” Michihisa & Hey Murakamii from MOONEYES, Japan
- Professional Japanese Drifter Daigo Saito from Fat Five Racing
- Katie’s Customs, Japan featuring a custom Vincent Black Shadow motorcycle
- STOOP Motorcycles, Japan – featuring a custom Harley-Davidson Panhead
- EVILACT, Japan featuring a custom 1947 Harley-Davidson Knucklehead EL
- Nigel Petrie from Engineered To Slide, Australia
- Spinny, Thailand – Best European Custom Bike Winner at Bangkok Hot Rod Show 2024
- Little Boy Cycles, Thailand – Best of Show Winner at Bangkok Hot Rod Show 2024
- Dino Dalle Carbonare & Alexander Iain from Speedhunters.com, Global
- ONE LOW, Masashi Tasaki; Japan
- Tengku Djan Ley, The Malaysian Prince of Drift
- Makoto from Makoto M&K Custom Signs, Japan
- 2 Percenter, Japan
- Masanari Kobyashi, Japan
- Burnout Magazine, Japan
- Vibes magazine, Japan
- Ignite magazine, Thailand
- Cynar, Japan
- Mow, Australia
- Choppajoop, Singapore
- Sixty Sick Paintlab, Indonesia (a collective group of 15 pinstripe artists)
- Fahmi Freeflow, Indonesia
- Mill Art, Indonesia
- Pinman, Thailand
- Irvine Jasta, Indonesia
- Cherry Bomb Pin-Up Parlour, Singapore
- Bangkok Hot Rod Show, Thailand
- Mooneyes Bangkok, Thailand
- Kustomfest, Indonesia
- Borneo Kustom Show, Brunei
- BBQ Ride, Indonesia
- Wicked Wallop, Singapore
- Ya Seat, Thailand
- Wheelspin, Thailand
- Von Dutch, Indonesia
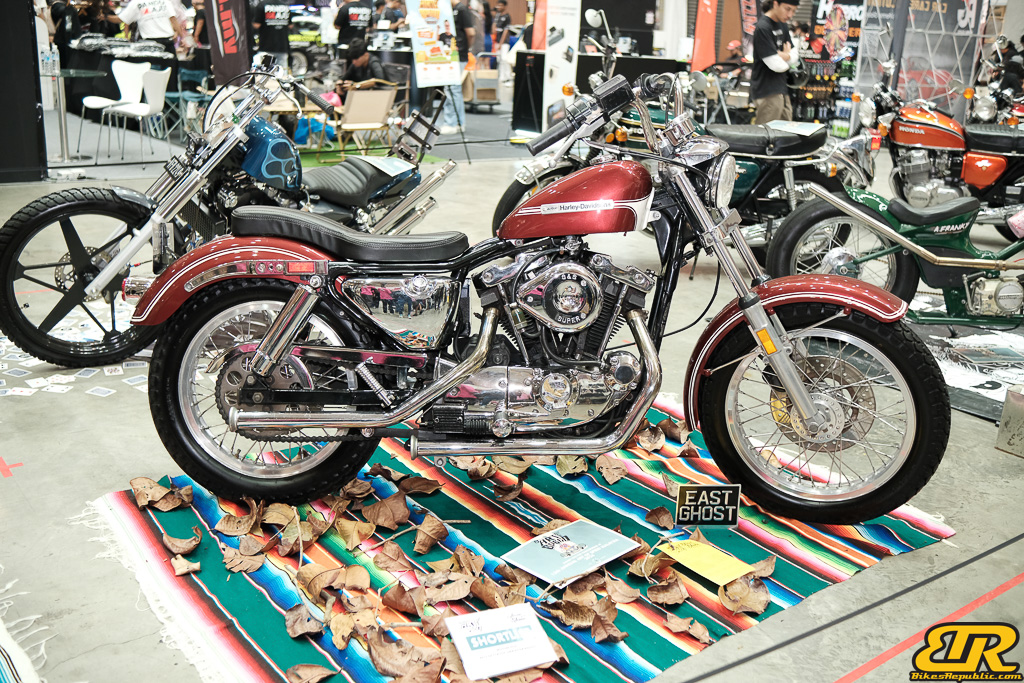

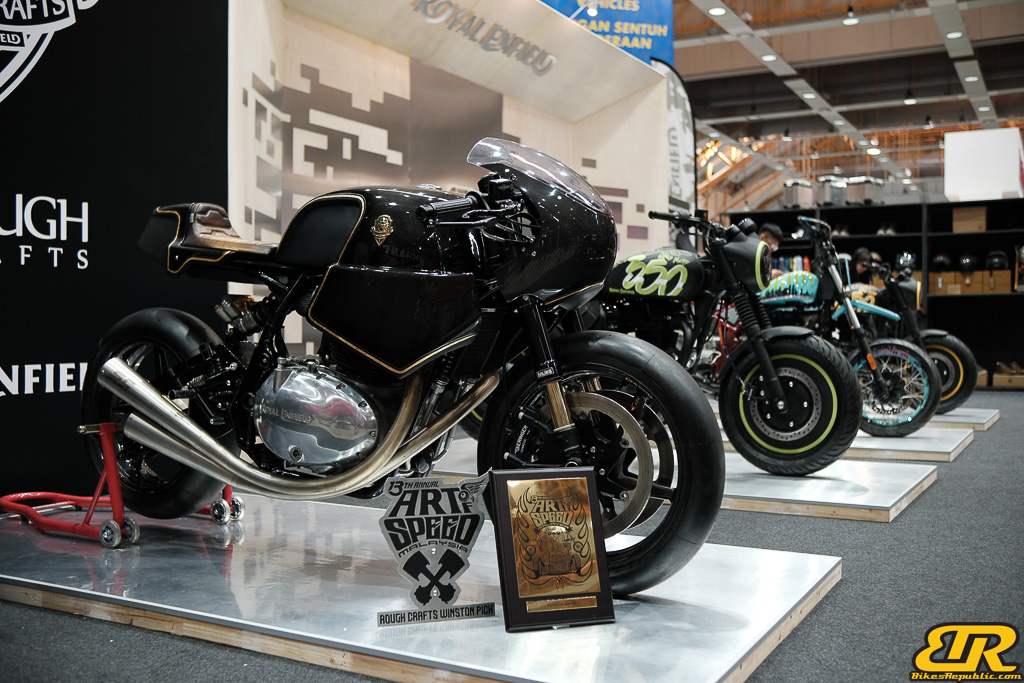
This year’s Art of Speed Invitational Bike Build Off 2024 featured 10 talented builders competing to wow the jury selection and public choice. The overall jury pick winner and public choice were unanimously awarded to Irwann Cheng from FNG Works with their amazing RXZ Twin Boss V2. FNG Works took home a RM5,000 cash prize for the public choice and will have their custom bike shipped to Japan for the 32nd Annual MOONEYES Yokohama Hot Rod Custom Show 2024 as the jury pick winner.

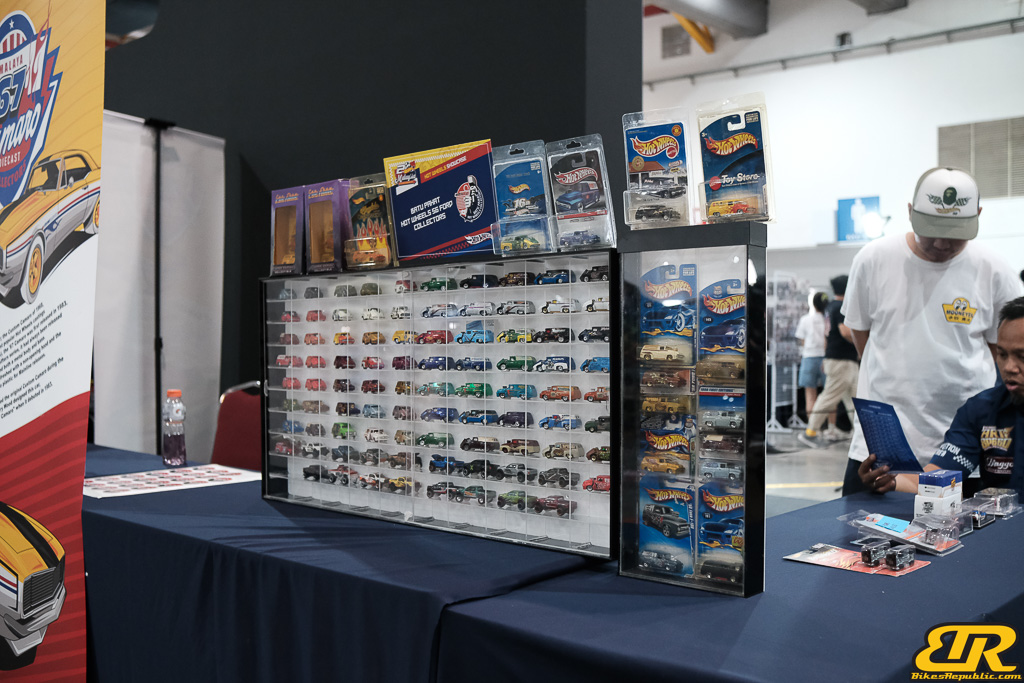
The 2nd Official Hot Wheels Collectors Convention Malaysia was once again held at Hall C for fans and collectors of the die-cast brand. AOS 2024 marked the launch of the first ever convention exclusive die-cast model from Mattel factory for Malaysia together with Hot Wheels Design Manager – Vehicles, Dwayne Vance.
AOS 2024 also marked a special collaboration with Selangor FC (SFC) in support of SFC’s campaign; “Stop The Violence” crossing over from football to automotive lifestyle. Selangor Menteri Besar Datuk Seri Amirudin Shari attended the event on Sunday to officiate the collaboration and was given a special tour of AOS 2024.

Other AOS 2024 activities included:
- Roda Rumble 2024 – Two Wheels Gathering & Outdoor Festival supported by Retro Mania
- La Cultura – Malaysia’s Chicano Culture Appreciation Gathering, which includes a fashion display of Cholo and Chicano style, Dance and DJ show, and more
- Food Park food vendors and trucks
- Automotive flea market
- Product launching on stage
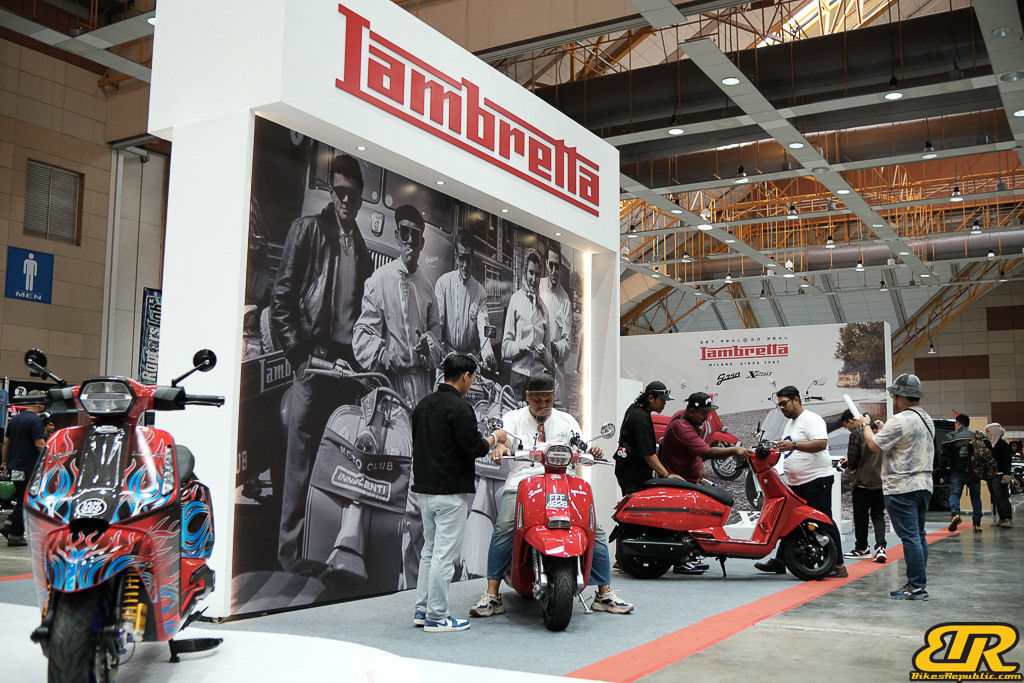
- Test Ride Zone for bike (Royal Enfield, Vespa, Aprilia, Triumph, Lambretta, Harley-Davidson, and more)

Instead of the usual outdoor festival, this year the SoundCircus Takeover returned as an indoor experience in Hall A. The SoundCircus Takeover line-up included Spider, Gerhana Ska Cinta, Salam Musik, Jemson X Forcesparkbois, Slatan, 53 Universe and many more.

Last but not least was the crowd favourite lucky draw giveaway. On Saturday, the giveaway was for ONE (1) paid Japan trip to the 32nd Annual MOONEYES Yokohama Hot Rod Custom Show 2024. The lucky winner of the Japan trip was awarded to Fitri Wahyudi B Suparno. On Sunday the grand prize for AOS 2024 was ONE (1) modified Honda Jazz in collaboration between AOS X QARTEL TV. This year’s lucky winner of the giveaway was awarded to Muhammad Farish B Mohd Fadzil.

The Best of Show motorcycle winner will win a package trip to the 32nd Annual MOONEYES Yokohama Hot Rod Custom Show 2024 as the Guest of Honour.
AOS SPECIAL AWARD
BEST OF SHOW MOTORCYCLE
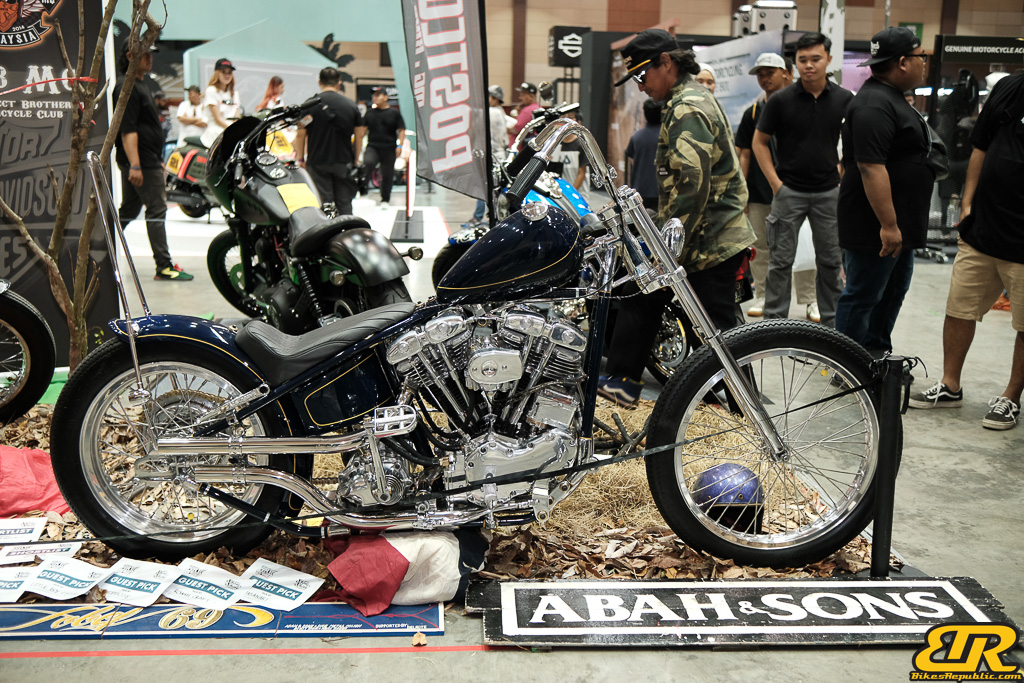
Winner : PA’DIN MUSA – Malaysia
Vehicle model : HARLEY-DAVIDSON SHOVELHEAD 1969
INVITATIONAL BIKE BUILD OFF
- Abah & Sons (Padin Musa)
- Nodie Cycles
- Acid Welding
- Zuhalfast
- RGF
- Flying Loser
- Chaos Customs
- FNG Works
- Hills Angels
- Son of Abdul

PUBLIC CHOICE AWARD
Winner : FNG WORKS – IRWANN CHENG
Vehicle model: RXZ TWIN BOSS V2
JURY PICK WINNER
Winner : FNG WORKS – IRWANN CHENG
Vehicle model : RXZ TWIN BOSS V2
CUSTOM KINGS BY HARLEY-DAVIDSON
First Runner Up : NORKHAIRI – Malaysia
Winner : KHAIRUL AZIMIN – Malaysia

List of AOS2024 winners:
Winner : NANOSTIX – Malaysia
Winner : BWB – Malaysia
Winner : HILLS ANGELS – Malaysia

Invited Guest Pick
Winner : ART GARAGE – Malaysia
- EVILACT PICK & KUSTOMFEST PICK
Winner : HILLS ANGEL – Invitational Bike Build Off – Malaysia
- STOOP MC PICK, LITTLE BOY CYCLES PICK, CHOPPAJOOP PICK, MASANARI PICK, ROUGH CRAFT PICK & BANGKOK HOT ROD PICK
Winner : PA’DIN MUSA – Malaysia
Winner : FNG WORKS – RXZ TWIN BOSS V2 – Malaysia
Winner : ASEP AHMAD ISKANDAR – ART OF SPEED FESTIVAL DIRECTOR
- SPINNY PICK, MR. PINMAN PICK, MOONEYES BANGKOK PICK & IGNITE BKK PICK
Winner : 1968 ANGELS – HILLS ANGELS – Malaysia
Winner : ALEX LIEW – Malaysia
Winner : 1950 CHEVY TRUCK – Thailand
Winner : 1941 DODGE TRUCK – Thailand
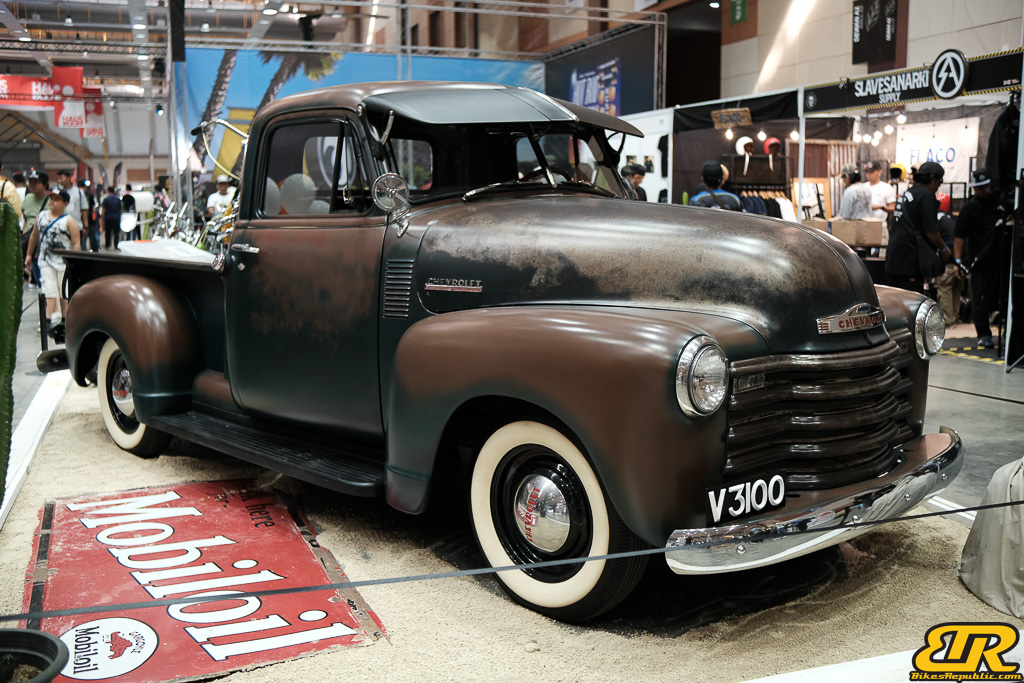

Winner : 1993 LIL’ BOOGIE – HILLS ANGELS – Malaysia
Winner : HOSNI MUBARAK – Malaysia
Winner : ACID WELDING – Malaysia
Winner : SHAMAN – Malaysia
Winner : AZIZAN – CHAOS CUSTOM – Malaysia
- SIXTY SICK PAINT LAB PICK
Winner : RUSTY FACTORY – Malaysia
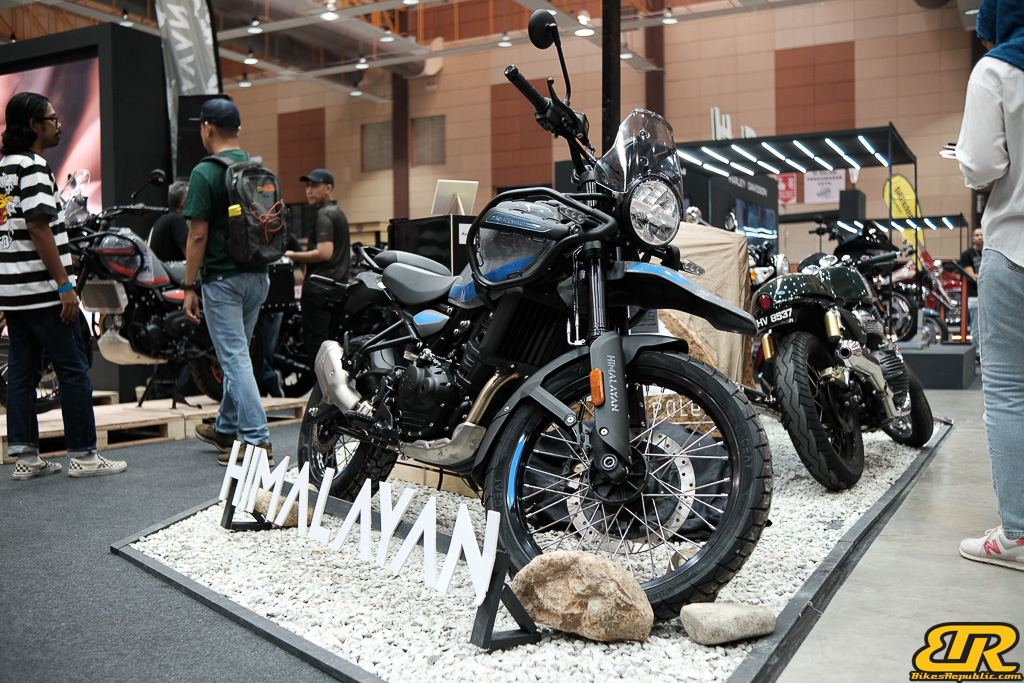

Winner : 1948 RUN HONEY RUN – HILLS ANGELS – Malaysia
Partner Pick
Winner : NIGEL PETRIE – ENGINEREED TO SLIDE
Winner : REINIER KISWANSURIZK – Malaysia
- MATTEL CONTINENTAL ASIA SDN BHD PICK
Winner : MUHAMAD REDUAN SAMNSUDIN – Malaysia
Winner : EAST GHOST MC – Malaysia
- HARLEY-DAVIDSON Malaysia PICK
Winner : HILLS ANGELS – SHOW & SHINE – Malaysia
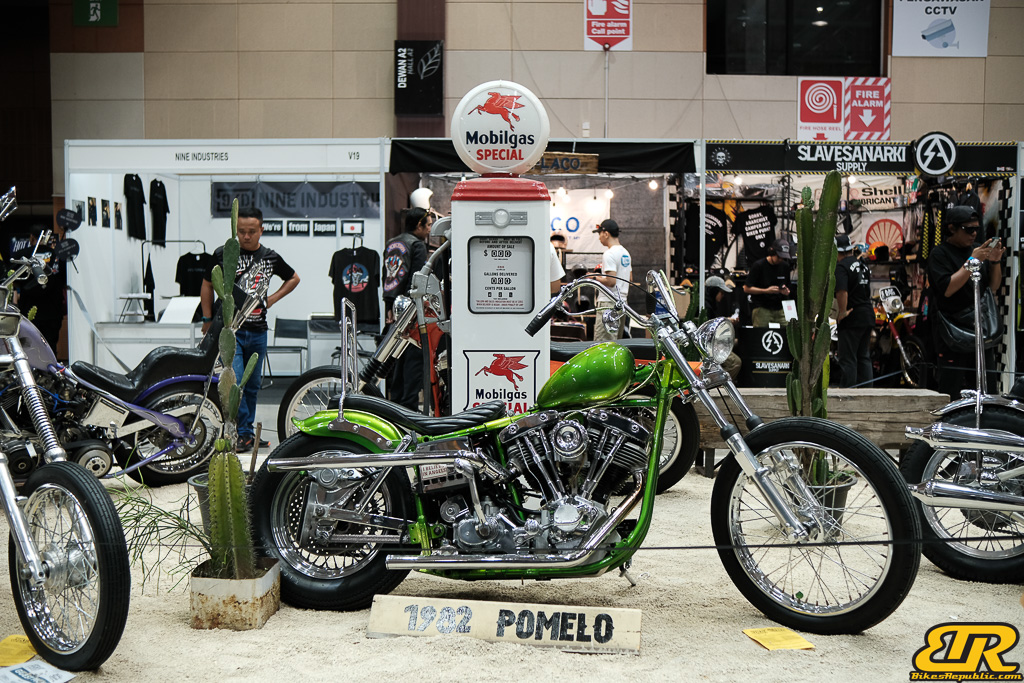

Winner : ABAH & SONS – SHOW & SHINE – Malaysia
- ROYAL ENFIELD PICK & TRIUMPH PICK
Winner : 1959 CHORRTORRO – Malaysia
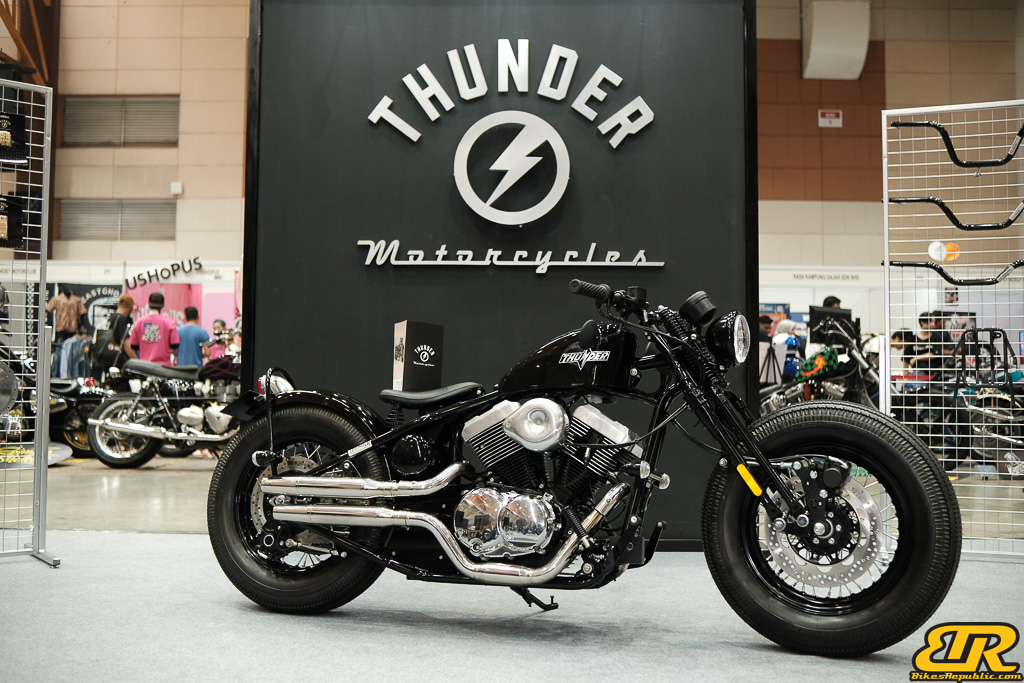
Winner : THUNDER MOTORCYCLES BOOTH – China
Winner : ROBERT MIDDLETON – Malaysia
Winner : IGL COATINGS X FAT JOE’S PRESTIGE TOUCH- Malaysia
AOS2024 Show & Shine winners
LOWRIDER CATEGORY
- BEST OF LOWRIDER – 12″, 16″ & 20″ WHEEL LOWRIDER
Winner : SHAM ENERGYCOM – DOUBLE DICE CREW – Malaysia
- BEST OF LOWRIDER – 24″, 26″ & OPEN WHEEL LOWRIDER & LIMOUSIN
Winner : MAT TOPO – DOUBLE DICE CREW – Malaysia
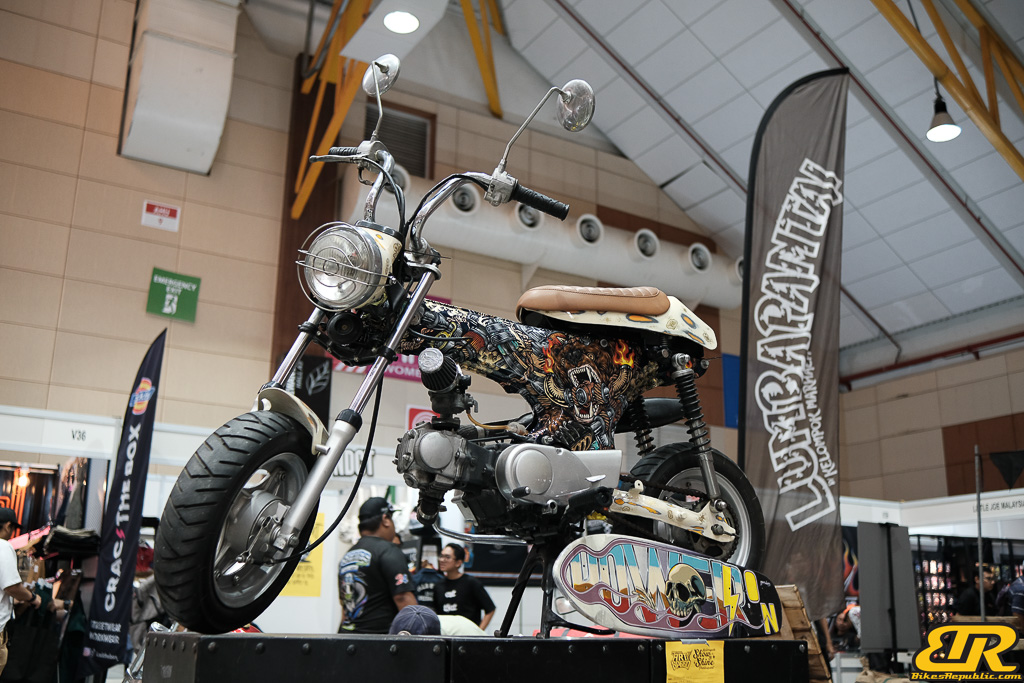

Winner : MEGAT PANJI ALAM – Malaysia
Winner : RAISYA KIDD – DOUBLE DICE CREW – Malaysia
Winner : SAHRIL SALLEH – Malaysia
Winner : ASYRAF – DOUBLE DICE CREW – Malaysia
AUTOMOBILE
Winner : FAROIB AUTOSPORT – Malaysia
Winner : VOX – Malaysia
Winner : SHAMAN – Malaysia
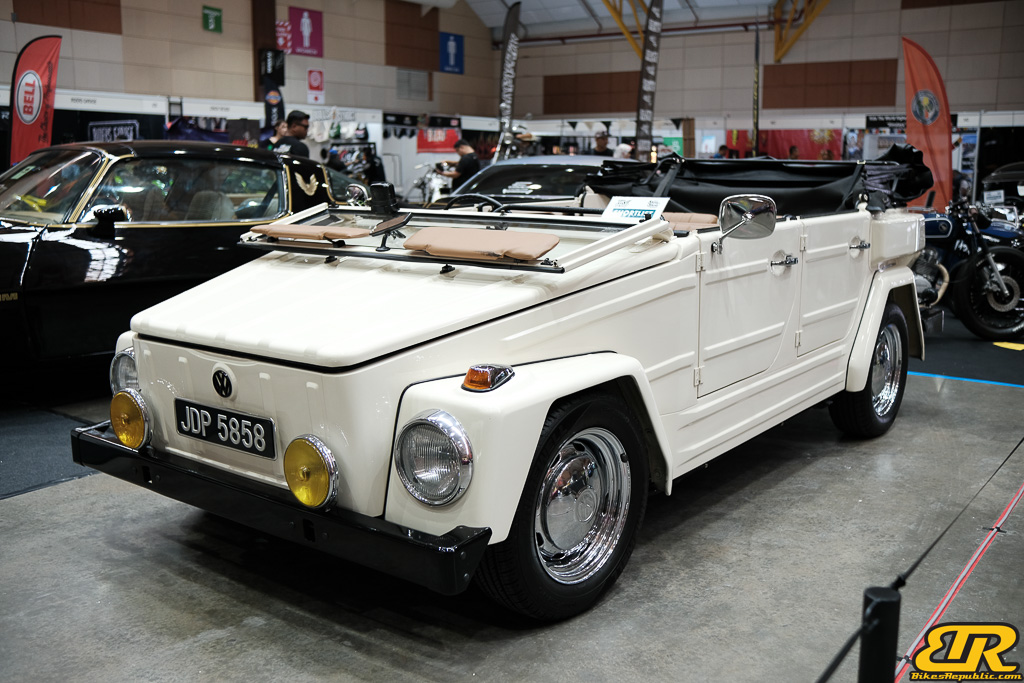

Winner : TOMMY – Malaysia
Winner : CREZTA – Malaysia
Winner : AMER HARRIS – Malaysia
Winner : NOISY BOY – Thailand
Winner : ART GARAGE – Malaysia
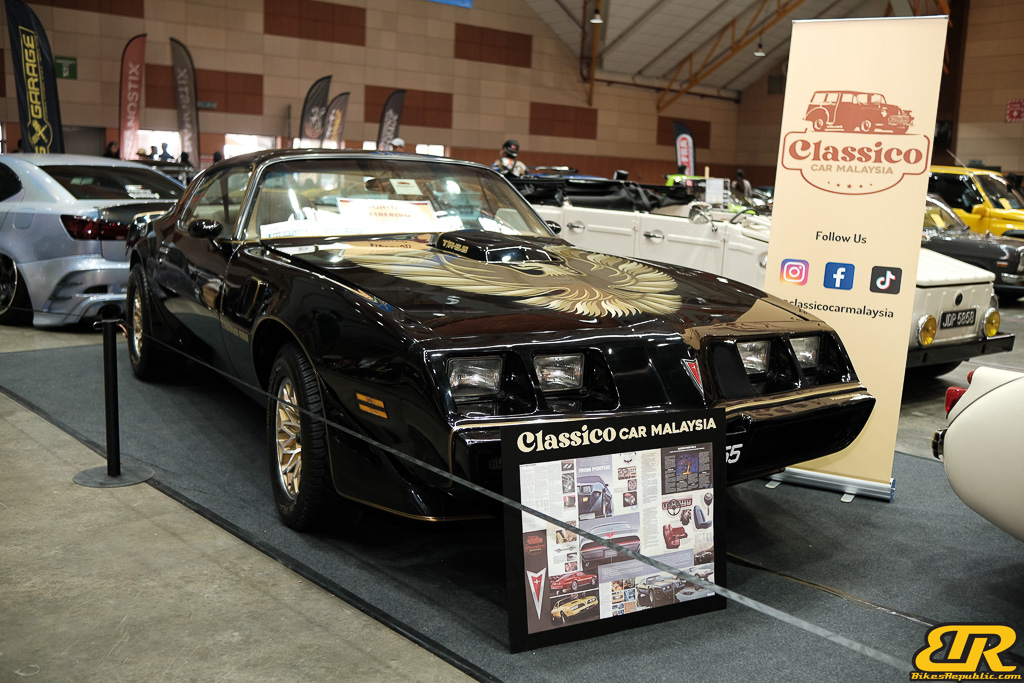

Winner : WING HIN – Malaysia
Winner : MOHD FAIZ ALI – Malaysia
Winner : BAY BWB – Malaysia
Winner : AXLED GARAGE – Malaysia
Winner : EDDY NEO – Malaysia
Winner : EDRY AMYRUL – Singapore
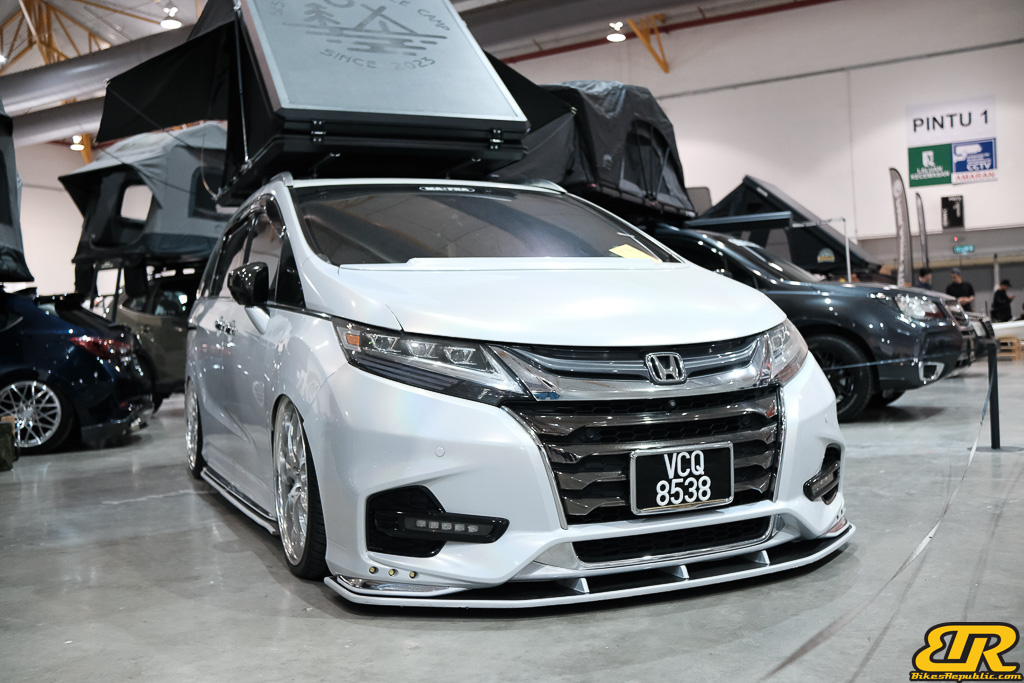

Winner : WAN IBRAHIM WAN HASSAN – Malaysia
Winner : HAZUAR FROM BIG CAT CUSTOM – Malaysia
Winner : PRAJAK TANTIKULWIJIT – Thailand
Winner : ART GARAGE – Malaysia
Winner : TOMMY – Malaysia
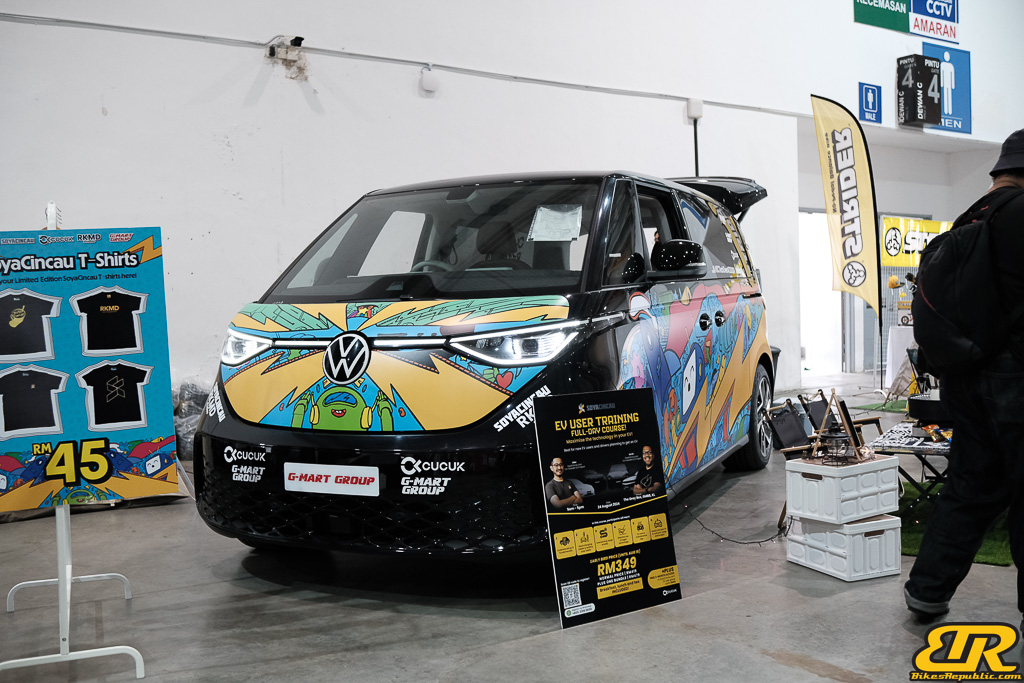

Winner : ADY BWB – Malaysia
Winner : TOM CLASSIC – Thailand
Winner : MUUHAMMAD FIKRIE – Malaysia
Winner : FAROIB AUTOSPORT – Malaysia
Winner : HAZUAR FROM BIG CAT CUSTOM – Malaysia
Winner : REJAB AUTOSPA – Malaysia

MOTORCYCLE
- BEST OF CHOPPER ABOVE 401CC
Winner : PA’DIN MUSA – Malaysia
- BEST OF CHOPPER BELOW 400CC
Winner : KHAIRUL AMEER, BRAIN HUNDRED – Malaysia
- BEST OF CAFE RACER BELOW 400CC
Winner : HUZAIL ANAQI – Malaysia
- BEST OF JAP STYLE & TRACKER ABOVE 401CC
Winner : RUSTY FACTORY – Malaysia

- BEST OF JAP STYLE & TRACKER BELOW 400CC
Winner : RUSTY FACTORY – Malaysia
- BEST OF MODERN HARLEY-DAVIDSON
Winner : MAF14 AIRBRUSH STUDIO – Malaysia
- BEST OF CLASSIC HARLEY-DAVIDSON
Winner : EAST GHOST MC – Malaysia
Winner : NAZRAN ASFAHIM – Malaysia
Winner : MEOR AMIR FAIZAL – Malaysia

Winner : MOHAMMED FITRI ABDUL – Malaysia
- BEST OF CLASSIC CONTINENTAL
Winner : AZBEDER CYCLEWORK – Malaysia
- BEST OF MODIFIED CONTINENTAL
Winner : 1959 CHORRTORO – Malaysia
- BEST OF ALL MAKES MODERN BIKE
Winner : RUDY GTB – LARRY TONNKA – Malaysia

- BEST OF TWIN SHOCK CHOPPER
Winner : RUSTY FACTORY – Malaysia
Winner : PA’DIN MUSA – Malaysia
Winner : SHOIRAZI SALLEH – Singapore
Winner : MOHD NAIM – Malaysia
Winner : JANDAL 68 – Malaysia
For more information about this event, please visit www.artofspeedmy.com or www.facebook.com/ArtOfSpeedMY/

13th Art of Speed 2024 photo gallery